(UroToday.com) The 2024 European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Annual Congress held in Barcelona, Spain between September 13th and 16th, 2024 was host to a session focusing on rare genitourinary cancers. Professor Andrea Necchi provided updates on the treatment of penile cancer.
In 2018, there were an estimated 2,080 new cases of penile cancer diagnosed in the United States, with 410 patients dying of this disease. However, penile cancer makes up only 0.4–0.6% of all malignancies in the U.S. and Europe and is, thus, an ‘orphan malignancy.’
Dr. Necchi noted the significant geographic variation in the incidence of penile cancer worldwide, with the highest incidence reported in South America, certain African countries, and India.
The surgical indications for an inguinal/pelvic lymph node dissection in patients with penile squamous cell carcinoma are based on the predictable clinical course of this disease. Summarized below are the indications for a pelvic and/or inguinal lymph node dissection, based on clinical and pathologic features.
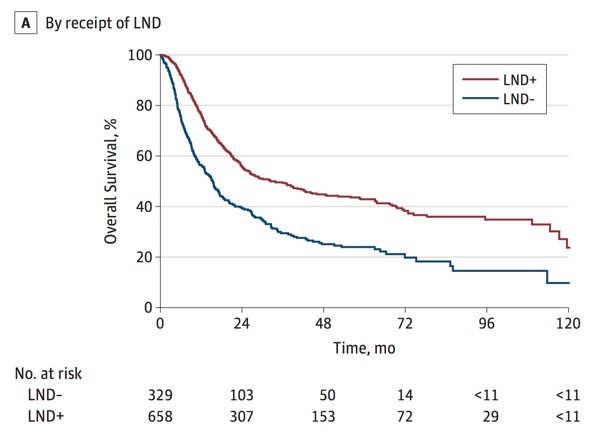
Over the last several years, there have been several studies assessing trends in the treatment of penile squamous cell carcinoma. Data from Joshi and colleagues looking at 1,123 patients with node-positive disease from the National Cancer Database (NDCB) between 2004 and 2014 demonstrated that the use of systemic chemotherapy significantly increased from 38% to 48%. However, only 53% of patients with cN3 disease received chemotherapy. 67% of patients underwent a lymph node dissection. In this study, on multivariable analysis, inguinal lymph node dissection was associated with better overall survival, while neither chemotherapy nor radiotherapy was associated with an improvement in overall survival:2
The EAU-ASCO collaborative guidelines on penile cancer were recently presented at the 2023 EAU annual congress in Milan. Key updates highlighted by Dr. Necchi included the recommendation to ‘offer neoadjuvant chemotherapy as an alternative approach to upfront surgery to selected patients with bulky mobile inguinal nodes or bilateral disease who are candidates for cisplatin and taxane-based chemotherapy’ (weak recommendation).
What are some ongoing challenges for the treatment of locally advanced penile squamous cell carcinoma patients? The selection of patients for perioperative therapy remains unclear and whether the efficacy of neoadjuvant/adjuvant therapy can be improved remains a question. For now, Dr. Necchi emphasized that enrolment in clinical trials remains the best option for these patients.
Summarized below are the chemotherapy regimens available to treat locally advanced penile squamous cell carcinoma. Dr. Necchi noted that a significant body of evidence originates from retrospective studies.
In 2010, Pagliaro et al published the results of a phase II trial of neoadjuvant TIP (paclitaxel, ifosfamide, and cisplatin) in 30 men with cN2-3M0 penile cancer without distant metastases. An objective response rate of 50% was observed (complete: 10%; partial: 40%), with an additional 30% having stable disease. The pathologic complete response was 10%. Twenty-two patients (73%) underwent a radical resection. The median time-to-progression was 8.1 months, and the median overall survival was 17 months.3
A systematic review of 10 studies and 182 patients receiving preoperative neoadjuvant chemotherapy for locally advanced penile squamous cell carcinoma was published in 2020. This demonstrated a pooled objective response rate of 53%, with a pathologic complete response of 16%. The pooled grade ≥3 toxicity was 40%. The overall mortality was 55%.4
In 2016, Nicolai et al published the results of a phase II trial of 47 N2–3M0 penile cancer patients who underwent neoadjuvant (n=28) or adjuvant (n=19) TPF (taxane, cisplatin, 5-FU). Following neoadjuvant therapy, 43% of clinical responses were observed, including 14% pathologic complete responses; however, responses were not associated with survival. Patients receiving adjuvant therapy had superior progression-free and overall survival, compared to those receiving neoadjuvant therapy.5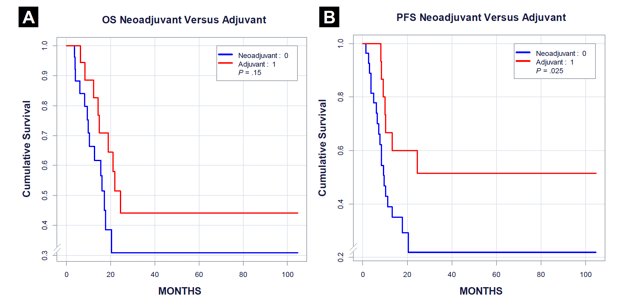
The International Penile Advanced Cancer Trial (InPACT) ECOG-EA8134 trial is currently evaluating the role of neoadjuvant therapy, including both chemotherapy and chemoradiation, in patients with cN1-3 squamous cell carcinoma of the penis with measurable disease by RECIST criteria. The InPACT trial design is as follows: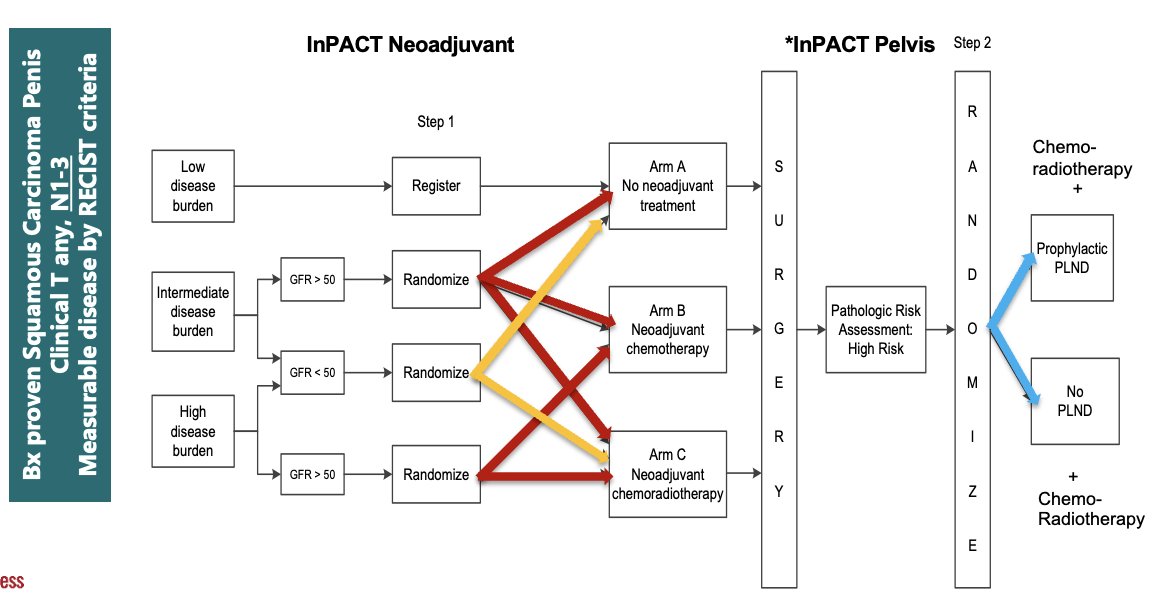
The primary trial endpoint is overall survival, with secondary endpoints including disease-specific survival, disease-free survival, distant metastasis-free survival, local recurrence-free survival, pN0 rate, toxicity, surgical complications, and feasibility of delivering treatment on schedule. The target accrual for InPACT is 400 patients across all international sites, including 200 in North and South America. With a target accrual of 200 patients, accrual from 2017 to 2023 has led to 114 patients enrolled in the trial, including 82 from the US and 32 from the UK. The target date for completing patient accrual is May 2024.
What about systemic therapy options in patients with metastatic or relapsed penile squamous cell carcinoma? Summarized below are the five treatment regimens available in this setting. Dr. Necchi highlighted vinflunine and dacomitinib which have demonstrated an objective response rate of ~30% in single-arm phase II trials.
Next, Dr. Necchi moved on to discuss human papillomavirus (HPV) in penile cancer. The overall incidence of HPV DNA in penile cancer is 42–70%, which is lower than cervical carcinoma (~100%) and similar to vulvar carcinoma (~50%). The prevalence of HPV differs by the penile cancer histologic subtype:
- 100% of warty subtypes
- 80% of basaloid
- 35% of keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma
- 33% of verrucous carcinoma
HPV infection status can be used to stratify patients into two groups with differing tumor immune microenvironments: HPV-positive versus HPV-negative penile squamous cell carcinoma: lower PD-L1 expression & higher median tumor mutational burden. Notably, the HPV viral protein E7 can directly inhibit RB and p21, leading to the accumulation of p16, which is associated with a better prognosis.
Overall, it appears that HPV+ patients have superior survival outcomes. An international multicenter series of 507 patients with penile squamous cell cancer who underwent an inguinal nodal dissection +/- chemotherapy or radiotherapy for the involved nodes demonstrated that HPV+ patients had lower cN stage and inguinal lymph node metastasis density (p<0.001 for both). HPV+ patients had superior overall survival in both the general cohort and in those receiving concurrent radiotherapy.6
To date, there is no definitive prospective evidence to support the efficacy of the quadrivalent HPV vaccine for the prevention of penile intraepithelial neoplasia (PeIN) or penile cancer. The seminal publication by Giuliano et al published in 2011 in The New England Journal of Medicine demonstrated that the efficacy of this vaccine against condylomata acuminata in the per-protocol population was nearly 90%.7
What about tumor mutational burden (TMB)? Among pelvic squamous cell carcinomas, the frequencies of TMB ≥10 mut/Mb cases are the following:
- Advanced penile squamous cell carcinoma: 15%
- Male anal squamous cell carcinoma: 24%
- Cervical squamous cell carcinoma: 27%
- Female anal squamous cell carcinoma: 22%
- Vaginal squamous cell carcinoma: 28%
The majority of penile tumors are considered TMB-low (85%), whereas 10% and 5% are known to be TMB-intermediate and high tumors, respectively. It is estimated that approximately 7% of penile squamous cell patients have an underlying germline mutation.8
Recently, both single-agent immunotherapy and immunotherapy combination regimens have been evaluated in advanced/metastatic penile cancer patients. In a cohort of 120 patients with locally advanced or metastatic disease, including nine with penile cancer, the combination of cabozantinib + nivolumab + ipilimumab was associated with a partial response in 4/9 patients, with the remaining five patients having stable disease.9
Results of the phase II PERICLES study were published in 2023.10 This was a single-center, non-randomized phase II trial of 32 patients with advanced penile cancer who received atezolizumab +/- radiation. This trial failed to meet its primary endpoint of 1-year progression-free survival (12.5%; target: ≥35%). The median overall survival was 11.3 months. The objective response rate was 17% (complete: 7%; partial: 10%). Improved progression-free survival was observed in patients with high-risk HPV-positive tumors (p=0.003) and those with high infiltration of intratumoral CD3+CD8+ T cells (p=0.037).
The phase II ORPHEUS trial was a single-arm, multicenter, phase II trial in 18 patients with advanced/metastatic penile squamous cell carcinoma, previously untreated with anti-PD-1/anti-PD-L1 agents. Patients received retifanlimab 500 mg intravenously every 4 weeks for up to two years. At a median follow-up of 7.2 months, the objective response rate was 17%, with a median duration of response of 3.3 months. The median progression-free survival was 2 months, and the median overall survival was 7.2 months. There were no grade 3–4 immune-related adverse events.11
The HERCULES trial (LACOG 0218) was recently presented at ASCO 2024. This is a Brazilian phase II, single-arm trial evaluating pembrolizumab + platinum-based chemotherapy as first-line treatment in advanced penile squamous cell carcinoma. Patients with metastatic or locally advanced disease (recurrent or TanyN3M0 or T4NanyM0) not amenable to curative-intent therapy received 5-FU + cisplatin + pembrolizumab for 6 cycles, followed by pembrolizumab for up to 34 cycles. The trial design is as follows: 
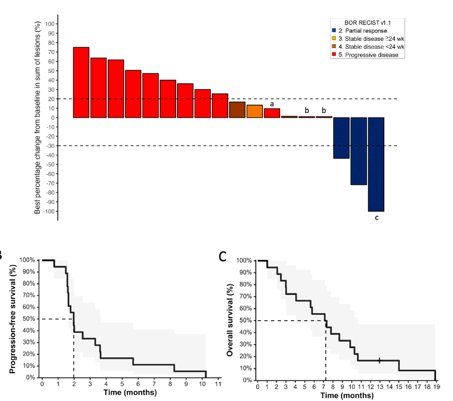
From August 2020 to December 2022, 37 patients were enrolled in 11 Brazilian centers and 33 patients were eligible for efficacy analysis. 65% of patients had metastatic disease, 22% had recurrent disease, and 14% had locally advanced disease. The confirmed overall response rate by investigator assessment was 39%, with 1 complete response and 12 partial responses. 
Tumor shrinkage of any magnitude was observed in 76% of patients:

The median duration of response was 6 months, and the median time to response was 1.4 months. The median progression-free survival was 5.4 months, and the median overall survival was 9.6 months. 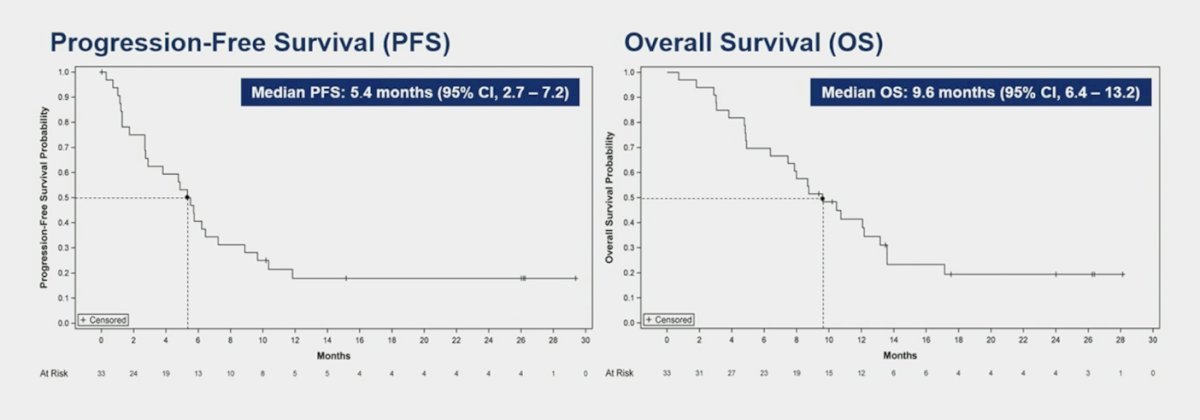
Responses were enriched in:
- TMB-high tumors: ORR: 75%
- HPV+ tumors: ORR: 55.6%
Grade 3-4 treatment-related adverse events were observed in 51.4% of patients (immune-related: 5.4%).
Additional novel neoadjuvant therapeutic strategies for penile squamous cell carcinoma patients are summarized in the schematic below: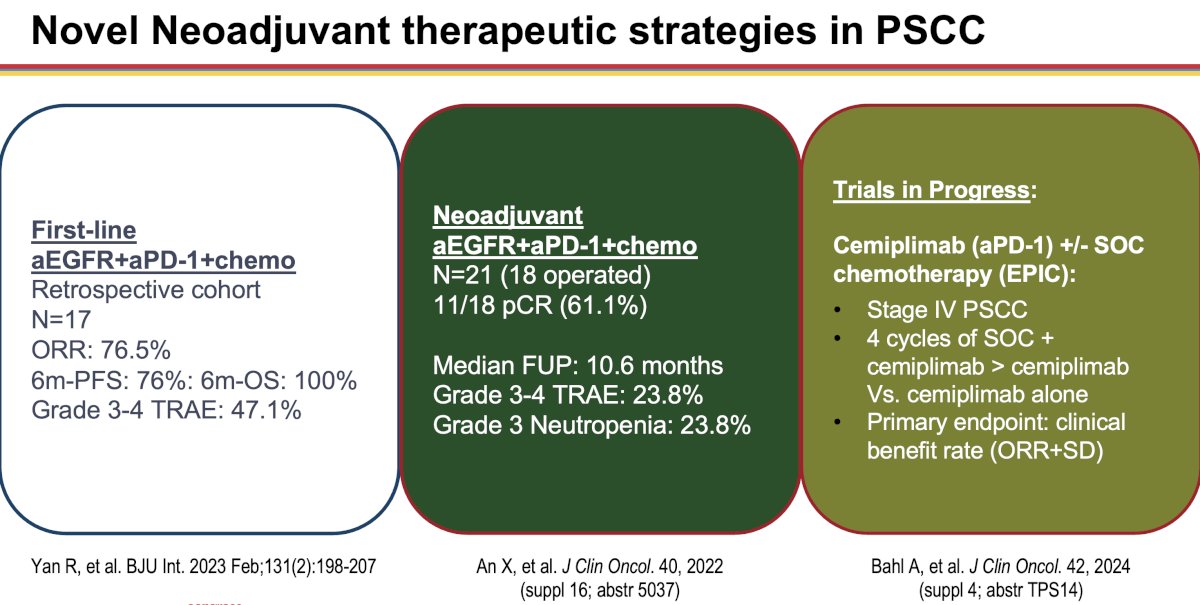
Dr. Necchi concluded his presentation as follows:
- Neoadjuvant chemotherapy: EAU/ASCO Guidelines and retrospective studies advise using neoadjuvant chemotherapy for unresectable or recurrent lymph node metastases (cN3) and select cN2 patients following thorough discussions
- Chemo-immunotherapy combinations may be an alternative option to TIP (in biomarker-selected patients)
- Trials: Basket trials including penile squamous cell carcinoma patients are needed in the post-chemotherapy setting
- We should start thinking of penile squamous cell carcinoma as multiple distinct biological entities
- TMB-high/HPV+ penile squamous cell carcinoma will deserve next-generation immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy-based trials.
Presented by: Professor Andrea Necchi, MD, Director of GU Medical Oncology, San Raffaele Hospital and Scientific Institute, Milan, Italy
Written by: Rashid Sayyid, MD, MSc – Robotic Urologic Oncology Fellow at The University of Southern California, @rksayyid on Twitter during the 2024 European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) Annual Meeting, Barcelona, Spain, Fri, Sept 13 – Tues, Sept 17, 2024.
References:
- Thomas A, Necchi A, Muneer A, et al. Penile Cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021; 7(1):11.
- Joshi SS, Handorf E, Strauss D, et al. Treatment Trends and Outcomes for Patients with Lymph Node-Positive Cancer of the Penis. JAMA Oncol. 2018 May 1;4(5):643-649.
- Pagliaro LC, Williams DL, Daliani D, et al. Neoadjuvant paclitaxel, ifosfamide, and cisplatin chemotherapy for metastatic penile cancer: a phase II study. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28(24):3851-7.
- Azizi M, Aydin AM, Hajiran A, et al. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis there a Benefit in Using Neoadjuvant Systemic Chemotherapy for Locally Advanced Penile Squamous Cell Carcinoma? J Urol. 2020; 203(6):1147-55.
- Nicolai N, Sangalli LM, Necchi A, et al. A Combination of Cisplatin and 5-Fluorouracil With a Taxane in Patients Who Underwent Lymph Node Dissection for Nodal Metastases From Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Penis: Treatment Outcome and Survival Analyses in Neoadjuvant and Adjuvant Settings. Clin Genitoruin Cancer. 2016; 14(4):323-30.
- Bandini M, Ross JS, Zhu Y, et al. Association Between Human Papillomavirus Infection and Outcome of Perioperative Nodal Radiotherapy for Penile Carcinoma. Eur Urol Oncol. 2021; 4(5):802-10.
- Giuliano AR, Palefsky AR, Goldstone S, et al. Efficacy of quadrivalent HPV vaccine against HPV Infection and disease in males. N Engl J Med. 2011; 364(5):401-11.
- Necchi A, Spiess PE, de Padua TC, et al. Genomic Profiles and Clinical Outcomes of Penile Squamous Cell Carcinoma With Elevated Tumor Mutational Burden. JAMA Netw Open. 2023; 6(12):E2348002.
- Apolo AB, Girardi DM, Niglio SA, et al. Final Results From a Phase I Trial and Expansion Cohorts of Cabozantinib and Nivolumab Alone or With Ipilimumab for Advanced/Metastatic Genitourinary Tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2024; 42(25):3033-46.
- De Vries HM, Rafael TS, Gil-Jiminez A, et al. Atezolizumab With or Without Radiotherapy for Advanced Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Penis (The PERICLES Study): A Phase II Trial. J Clin Oncol. 2023; 41(31):4872-80.
- Del Muro XG, Lopez-Bravo DP, Cuellar-Rivas MA, et al. Retifanlimab in Advanced Penile Squamous Cell Carcinoma: The Phase 2 ORPHEUS Study. Eur Urol Oncol. 2024: S2588-9311(24)00114-7.


