(UroToday.com) The second poster session at the 2022 International Kidney Cancer Symposium (IKCS): North America meeting featured a number of presentations, including one from Dr. Stephanie Berg examining novel treatment options in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
Both angiogenesis targeted therapies and immune checkpoint inhibitors have become standard first-line treatment options in advanced RCC, in combination therapy. However, there is an ongoing need to develop new therapeutic combinations and targets for the treatment of advanced clear cell (ccRCC). The cell cycle pathway is dysregulated in a significant proportion of ccRCC and pre-clinical studies have suggested that CDK4/6 inhibitors have both single-agent activity in ccRCC and synergism with IO. We hypothesize that a triplet with Axitinib, Palbociclib and Avelumab will have efficacy and demonstrate additive activity compared to the approved doublet of Axitinib and Avelumab.
To assess this, they designed a multi-center single-arm phase 2 trial (NCT05176288) the primary objective of which is to evaluate to objective response rate (ORR) per RECIST 1.1 of the triplet Axitinib, Palbociclib, and Avelumab in untreated advanced ccRCC.
The authors will include patients with untreated advanced ccRCC (sarcomatoid histology allowed) who have measurable disease per RECIST 1.1, adequate organ/marrow function, and an ECOG performance status of 2 or less. All IMDC risk groups are permitted. However, patients will be excluded if they have previously received systemic therapy, have untreated brain metastases, active autoimmune disease or a history of interstitial lung disease. Patients who have received adjuvant or neoadjuvant immunotherapy are eligible provided >12 months have elapsed.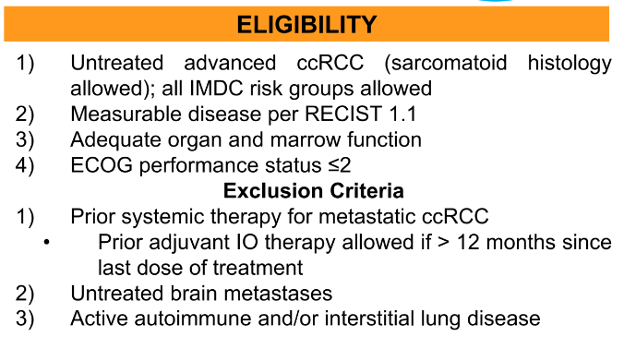
Beyond the primary outcome, the authors will assess the secondary objectives of safety, the rate of CR and deep PR (≥80% reduction in target lesions), and PFS and OS. Further, they will assess exploratory objectives including immunologic and biologic correlates of response, resistance, and survival with the triplet approach. Additionally, optional research biopsies will be performed as well as bulk whole-exome sequencing (seq) and single-cell RNA-seq to evaluate changes in gene signatures and immune cell populations during therapy. Alterations in candidate genes (cyclin D, CKD4, and CDK6) will be correlated with response to therapy.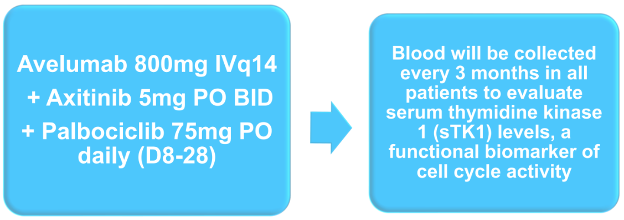
Additionally, blood will be collected to evaluate serum thymidine kinase 1 (sTK1) levels, a functional biomarker of cell cycle activity.
The planned sample size of 25 patients will provide 85% power to detect an improvement in ORR from 50% (seen with the doublet of axitinib and avelumab) to 75% with the triplet under the exact binomial test at a one-sided alpha of 0.05. The authors noted that this would provide a clinically meaningful signal to merit further study of this triplet.
Presented by: Stephanie Berg, DO, Loyola University Chicago, Chicago, IL


