(UroToday.com) The 2023 Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) Annual Meeting held in Chicago, IL between June 24th and 27th, 2023 was host to a session on urologic malignancies. Dr. Piyush Aggarwal presented the results of an analysis comparing early response assessment to tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in metastatic clear cell renal cell cancer (RCC) using 68Ga-PSMA-11-PET versus contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT).
Contrast-enhanced CT remains the guideline-recommended imaging modality of choice for primary tumor characterization, staging, and response evaluation for renal cell carcinoma (RCC). However, there are suggestions that contrast-enhanced CT underestimates the response to TKIs in patients with metastatic RCC, with response assessments commonly reported using the Response Assessment Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) v1.1 criteria. As such, there is an unmet need for enhanced imaging biomarkers to assess for early responses. The objective of this study was to evaluate the role of 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT as a potential angiogenesis imaging marker for predicting early response to anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-targeted therapy in metastatic clear cell RCC and compare its performance in this setting to contrast-enhanced CT (RECIST v1.1).
To this end, Dr. Aggarwal and colleagues conducted a prospective non-randomized, single-center observational study, which included consecutive adult patients with biopsy-proven metastatic clear cell RCC, who were planned for targeted first- and second-line treatments and had a life expectancy of >6 months. All patients underwent 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT at baseline, one month, and three months post-treatment initiation. Contrast-enhanced CT was performed at baseline and three months. Lesion positivity was assessed using both ’qualitative’ and ‘quantitative’ approaches:
- Qualitative: All lesions, except physiologic sites, with an increased uptake compared to the surrounding background were considered positive
- Quantitative: SUVmax, SUVpeak, PSMA-derived tumor volume (PSMA-TV), and total lesion PSMA (TL-PSMA)
68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT responses were assessed using the modified PERCIST 1.0 criteria, summarized in the table below:
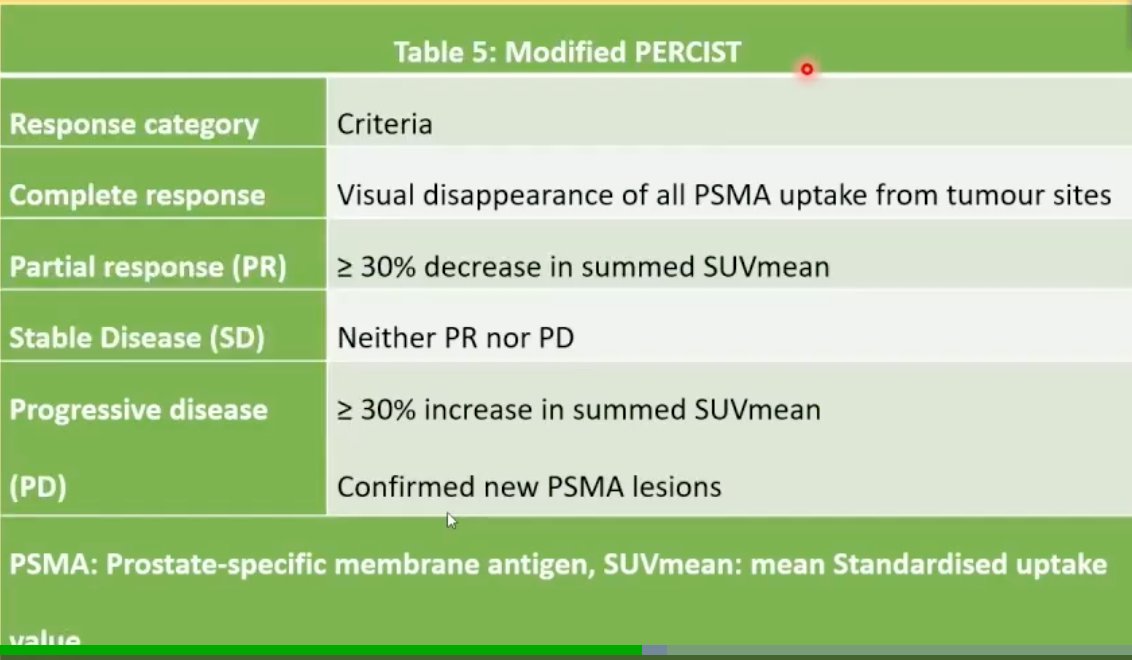
An objective response was defined as a partial or complete response, whereas stable or progressive disease were classified as a ‘non-response’. The concordance and discordance between PSMA PET and contrast-enhanced CT findings were quantified using Cohen’s Kappa statistic and McNemar’s test, respectively. Survival analysis using Kaplan Meier curves was employed to evaluate radiographic-progression-free survival, with between-group comparisons performed using the log-rank test.
This study included 21 patients, with a median age of 62 years. The authors evaluated the concordance of imaging findings between 1-month PET (i.e., PET performed one moth post-treatment initiation) and 3-months CT, as well as 3-months PET and 3-months CT.
- 1-month PET and 3-months CT
- Discordance: 12/21 patients (57%, p<0.001)
- Concordance: K=0.06, p=0.42
- 3-months PET and 3-months CT
- Discordance: 9/21 (43%, p=0.004)
- Concordance: K=0.25, p=0.08
Of the 21 patients, 13 (62%) progressed at a median follow-up of 19 months. The investigators next compared progression-free survival between responders and non-responders, stratified by the imaging modality used to ascertain response. Using 3-months contrast-enhanced CT for response assessment, there were no significant differences in progression-free survival between responders and non-responders.

Conversely, there were significant differences in PFS rates between responders and non-responders, when ascertained via either 1-month PET (p<0.001) or 3-months PET (p=0.012).
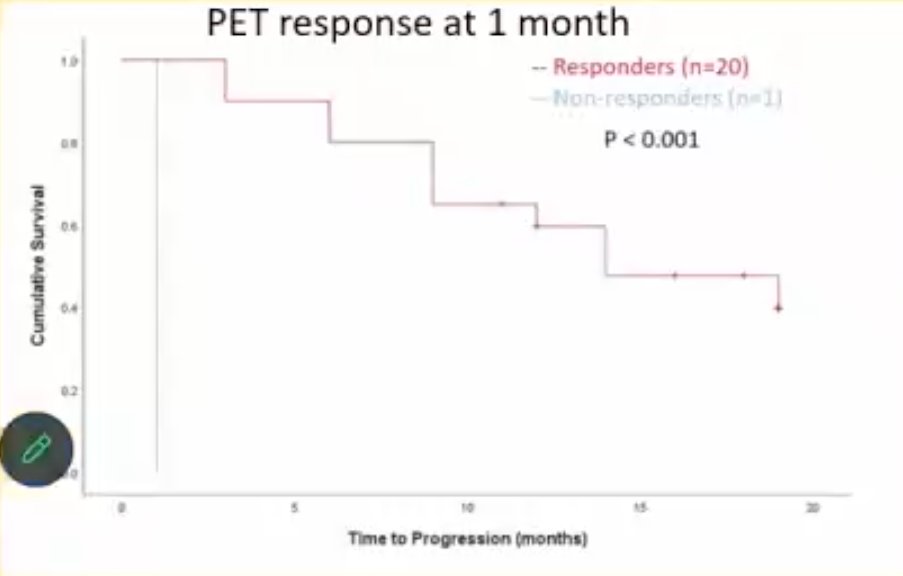
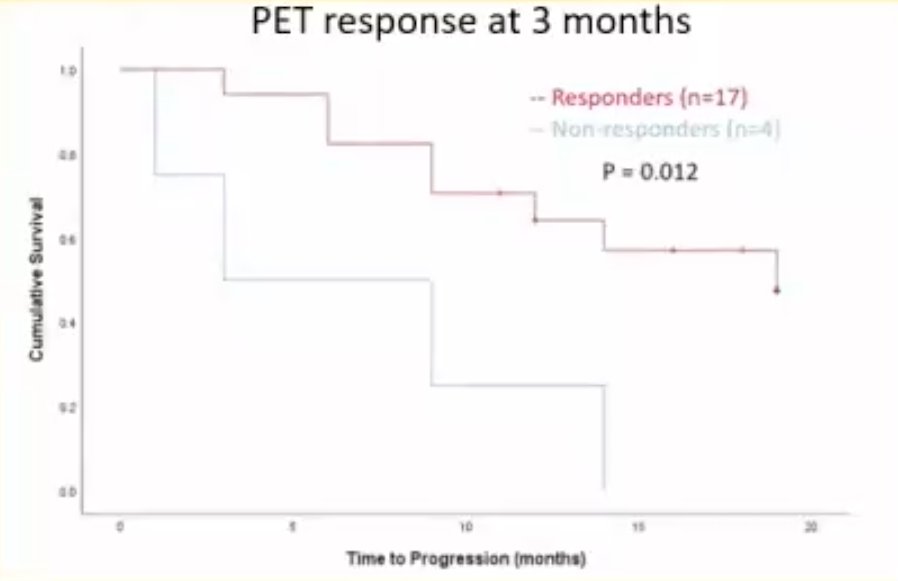
Next, the investigators evaluated ideal cut-offs for the baseline quantitative variables PSMA-TV and TL-PSMA for the prediction of survival outcomes among patients undergoing PSMA-PET at baseline. Using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves, they identified the following ideal cut-offs:
- PSMA-TV: 51.2 cm3
- TL-PSMA: 460.1
A significant difference in median PFS was observed between patients with high versus low PSMA-TV (6 months versus not reached; p<0.001) and TL-PSMA (9 months versus not reached; [<0.001). However, there were no significant differences in median PFS when baseline SUV parameters were evaluated.

Based on these results, Dr. Aggarwal concluded that early response assessment with 68Ga-PSMA-11- PET/CT is feasible and provides better results that conventional imaging using contrast-enhanced CT for metastatic RCC. As such, he suggested that 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT can be used to risk assess and guide early response-adapted treatment in metastatic clear cell RCC.
Presented by: Piyush Aggarwal, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (PGIMER), Chandigarh, India
Written by: Rashid K. Sayyid, MD, MSc – Society of Urologic Oncology (SUO) Clinical Fellow at The University of Toronto, @rksayyid on Twitter during the 2023 Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) Annual Meeting, Chicago, IL, Sat, June 24 – Tues, June 27, 2023.


