(UroToday.com) The 2023 SNMMI annual meeting included a prostate cancer session, featuring a presentation by Dr. Phillip Kuo discussing a post-hoc analysis of the LIGHTHOUSE and SPOTLIGHT studies to assess the impact of urinary activity on interpretation of 18F-rhPSMA-7.3 PET/CT. Radiohybrid (rh) 18F-rhPSMA-7.3 is a novel high affinity PSMA-targeting PET radiopharmaceutical currently under investigation as a diagnostic imaging tool for patients with prostate cancer:
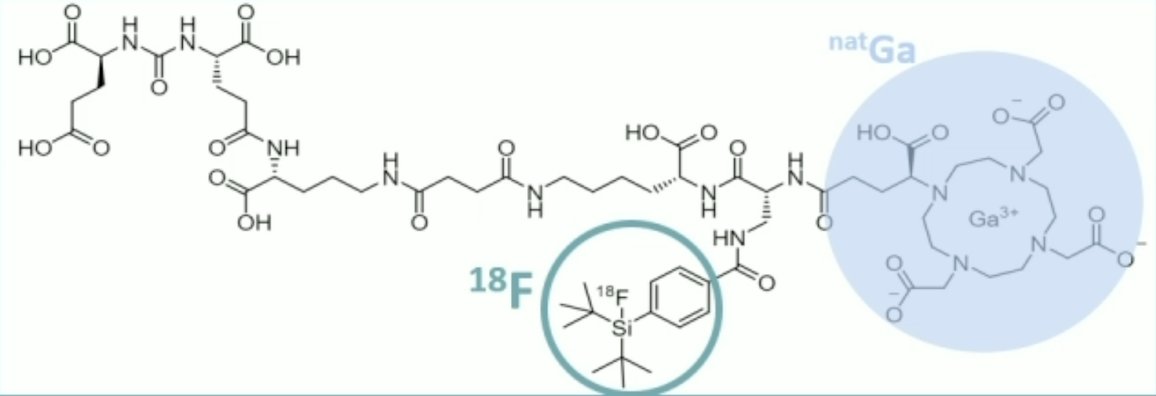
Early clinical data showed that 18F-rhPSMA-7.3 has lower average urinary excretion compared to other renally-cleared PSMA-PET agents and thus has potential to improve image evaluation in the prostate and peri-ureteric regions.1 The diagnostic performance of 18F-rhPSMA-7.3 has recently been investigated in two phase 3 studies: LIGHTHOUSE (NCT04186819) and SPOTLIGHT (NCT04186845). At the SNMMI 2023 annual meeting, Dr. Kuo and colleagues report results of a post-hoc analysis of all 18F-rhPSMA-7.3 scans acquired within these trials, to further assess the urinary tract activity of 18F-rhPSMA-7.3 and the influence on disease assessment.
Men with either treatment-naïve, newly diagnosed, unfavorable intermediate to very high-risk prostate cancer or with recurrent prostate cancer were enrolled in LIGHTHOUSE and SPOTLIGHT, respectively. All patients underwent PET/CT 50–70 min after IV administration of 8 mCi (296 MBq) ± 20% 18F-rhPSMA-7.3. For the present analysis, 718 18F-rhPSMA-7.3 scans (352 from LIGHTHOUSE and 366 from SPOTLIGHT) were re-evaluated by a single reader with 25 years’ nuclear medicine experience who had completed 18F-rhPSMA-7.3 reader training:
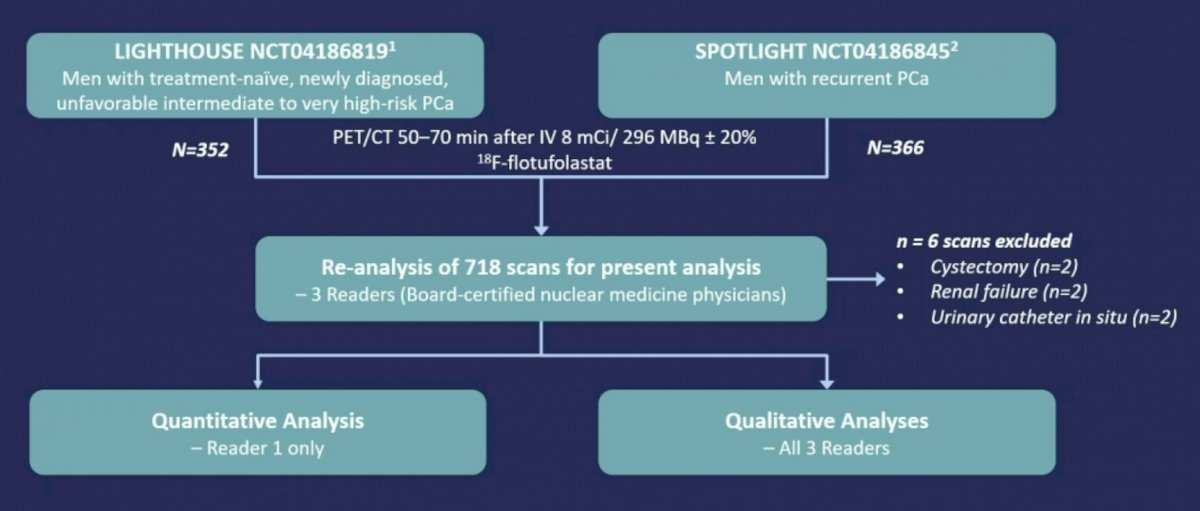
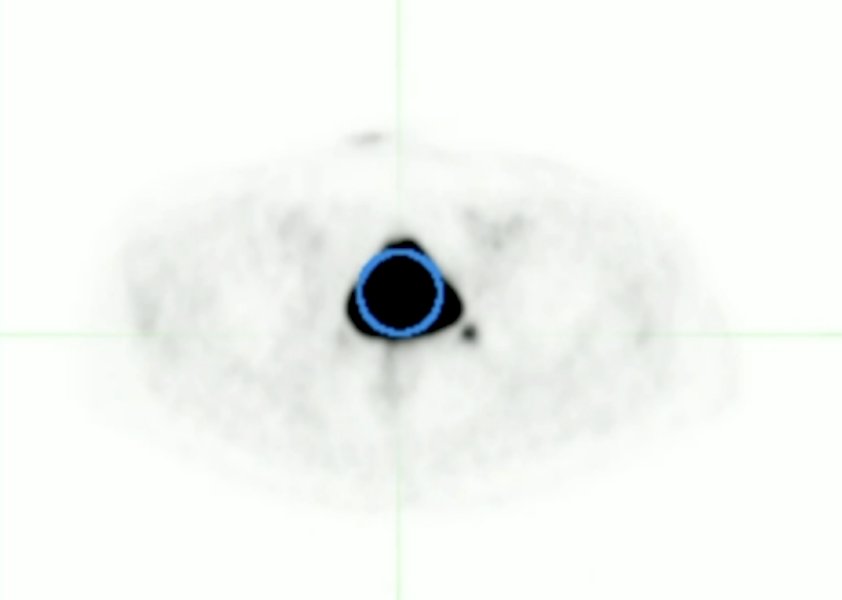
Quantitative assessments (SUVmax and SUVmean) of bladder activity were performed by placing a circular region of interest (ROI) over the maximum diameter of the activity in the bladder in the transverse plane:

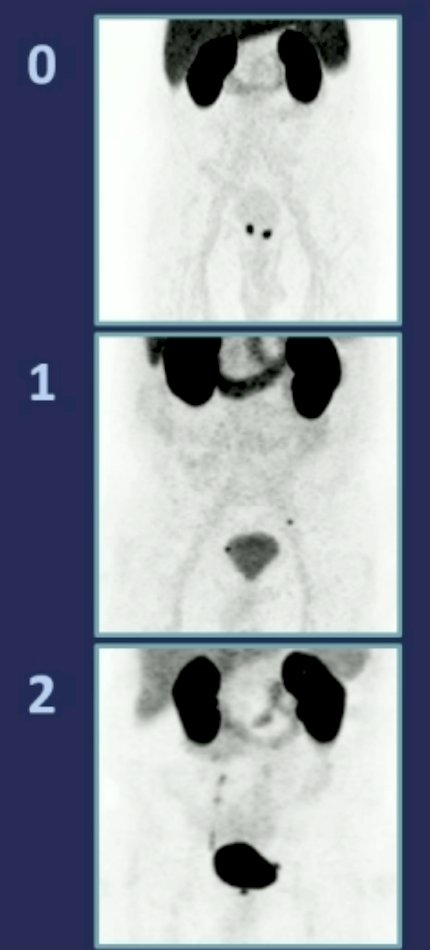
For qualitative assessments, the impact of any urinary excretion on the ability to assess the prostate/bed and pelvic/retroperitoneal lymph nodes, was evaluated using a 3-point scale:
- 0: no/minimally visible urinary activity
- 1: urinary activity visible but distinction between urine and disease possible
- 2: assessment inhibited by urinary activity
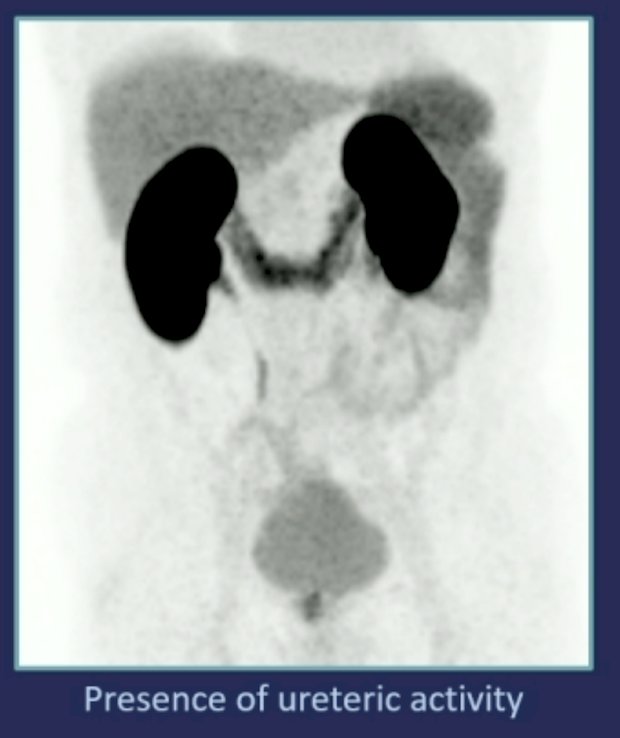
For ureteric activity (qualitative analysis), the presence or absence of a stasis of urine in keeping with ureteric activity was assessed. This was visualized on the MIP at a viewing window level of 0-10:
For the halo artifact (qualitative assessment), the presence or absence of a gross photopenic region around the bladder extending significantly beyond the bladder and overlying the other structures of the pelvis was assessed in the transverse slices:
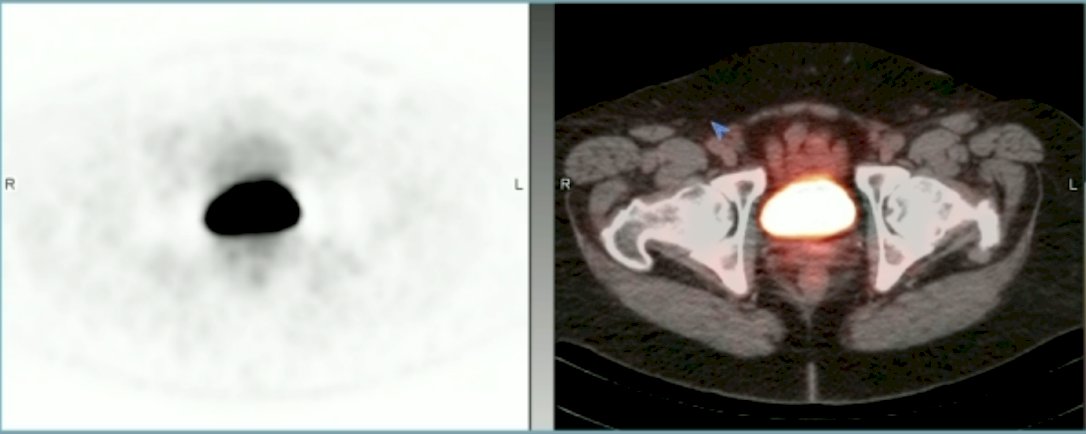
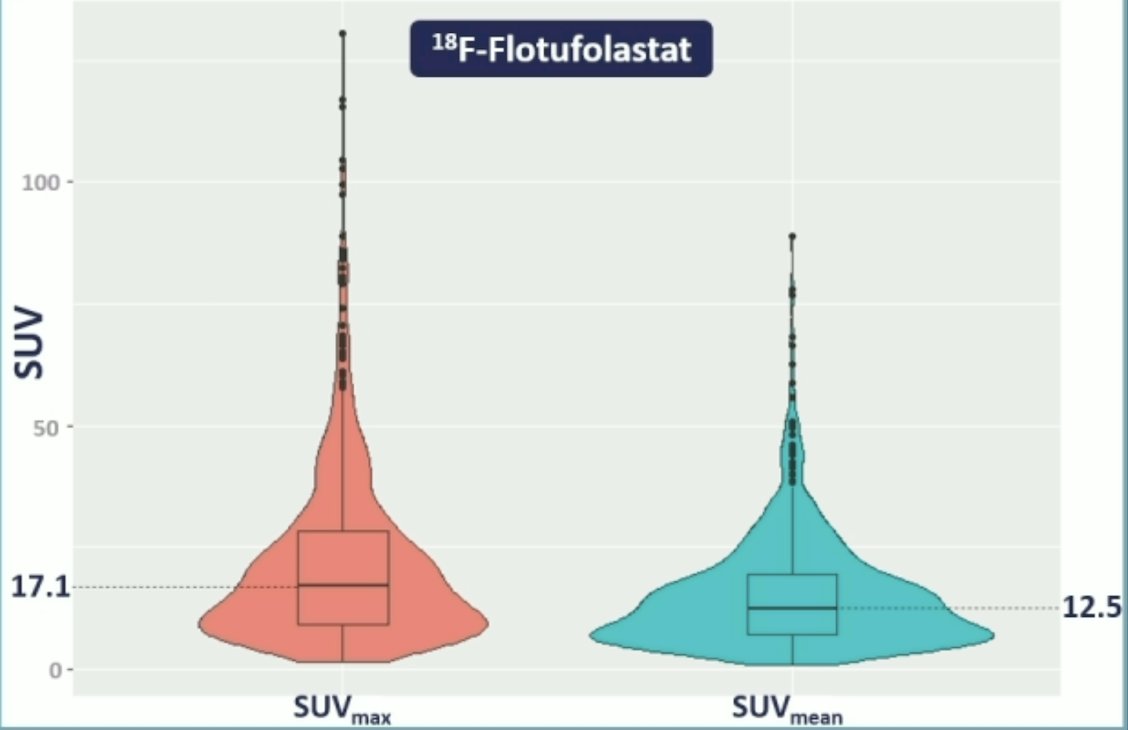
Among the 718 eligible scans, 712 (348 newly diagnosed prostate cancer and 364 recurrent prostate cancer) were evaluable for bladder activity with the reasons for exclusion being cystectomy (n=2), renal failure (n=2), or presence of a urinary catheter(n=2). The median SUVmax in the bladder was 17.1 (IQR, 9.2–28.3) and median SUVmean was 12.5 (IQR, 7.0–19.3):
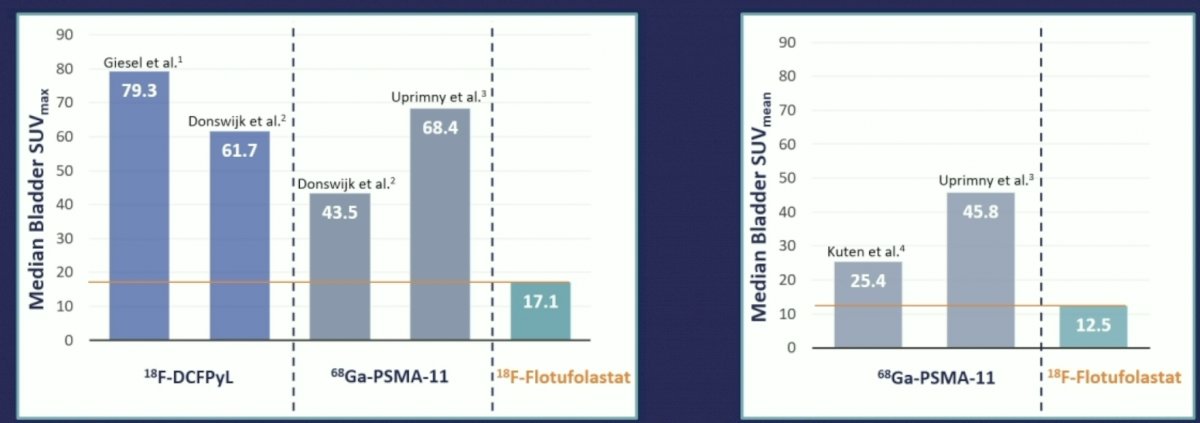
As follows is the median bladder SUVmax and SUVmean with reference to the published literature for renally-cleared PSMA PET agents:
Qualitative data showed that for 87% (616/712) of patients, it was possible to distinguish between urinary activity and disease uptake. In the minority of patients (13%, 96/712) where urinary activity did affect the assessment (rated 2), the median bladder SUVmean was found to be higher (19.7 vs 4.0 or 13.1 for those rated 0 or 1, respectively). Ureteric activity as defined by the presence of urine stasis was absent in 56% of patients by majority read. Finally, halo artifacts inhibiting assessment around the bladder were rare, occurring in only 0.3% of scans by majority read.
Dr. Kuo concluded his presentation discussing a post-hoc analysis of the LIGHTHOUSE and SPOTLIGHT studies to assess the impact of urinary activity on interpretation of 18F-rhPSMA-7.3 PET/CT with the following take home messages:
- Data from this post-hoc analysis of 18F-rhPSMA-7.3 scans from two prospective phase 3 trials show that the urinary activity of 18F-rhPSMA-7.3 is relatively low and does not influence disease assessment for the vast majority of patients
- Halo artifacts potentially inhibiting assessment occurred very rarely in this analysis
- Moreover, while this study was not designed as a head-to-head comparison, the median bladder SUVs compare favorably with values reported in the literature for other renally excreted PSMA-PET ligands
- The qualitative findings are being further investigated in a multi-reader analysis
Presented by: Phillip Kuo, MD, PhD, FACR, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ
Written by: Zachary Klaassen, MD, MSc – Urologic Oncologist, Associate Professor of Urology, Georgia Cancer Center, Augusta University/Medical College of Georgia, @zklaassen_md on Twitter during the 2023 Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) Annual Meeting, Chicago, IL, Sat, June 24 – Tues, June 27, 2023.
References:


