(UroToday.com) The Society of Nuclear Medicine & Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) 2024 Annual Meeting held in Toronto, ON between June 8th and June 11th, 2024 was host to a prostate cancer imaging session. Dr. Joseph Frankl presented the results of an analysis of primary lesion 68Ga-PSMA-11 total lesion activity as a highly sensitive predictor, with a concurrent high negative predictive value, of advanced-stage disease for the initial staging of patients with moderate to high-risk prostate cancer.
68Ga PSMA-11 PET/CT has demonstrated a sensitivity of 40–66%, with an associated negative predictive value of 81–86% for the detection of pelvic nodal disease when performed for the initial staging of prostate cancer patients.1,2 As such, negative PSMA-11 PET/CT findings cannot be used to reliably exclude the presence of pelvic nodal disease and omit a pelvic lymph node dissection. The primary objective of this study was to evaluate whether combining clinical parameters with PET/CT imaging findings can improve the diagnostic performance of PET/CT for the initial staging of patients with intermediate- to high-risk prostate cancer.
This was a retrospective analysis of 169 patients with intermediate- to high-risk prostate cancer who underwent staging with 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT between July 2021 and December 2022 at a single institution. Of the 169 study subjects, 29 (17.2%) were found to have metastatic disease. These 29 subjects, along with an additional 40 randomly selected subjects without evidence of metastatic disease, were included in the final study cohort for data analyses.
The reference standard was histopathology, when available, otherwise, PET/CT results served as the reference standard based on clinical interpretation with an overread by an experienced nuclear medicine physician and clinical follow-up for up to 12 months. The scan protocol included the administration of 185 MBq IV of Ga-68 PSMA-11, followed by a slow push of 20 mg furosemide, and a 60-minute uptake time. Scans were conducted using either a Siemens Biograph or GE 5-ring Discovery MI.
The following patient-level variables were collected:
- PSA level
- Grade Group
- Primary SUVmax (L-SUV)
- Primary/aorta SUVmax ratio (L/A SUVr)
- Primary PSMA total lesion activity (L-TLA)
- L-TLA could be derived from a single lesion or as the sum of individual lesions within the prostate (e.g., L-TLA1 + L-TLA2 + L-TLA3), calculated as the averaged SUV multiplied by volume
- PSA/L-TLA ratio
- PSA/total-prostate TLA (PSA/TP-TLA ratio)
- TP-TLA was defined as the sum of primary TLA (L-TLA) and normal-prostate TLA (NP-TLA), both based on a 41% cut-off of SUVmax.
Syngo. via VB60A, Siemens Healthineers, was used for the assessment of imaging parameters. Statistical tests included receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analyses, logistic regression modeling, and Spearman’s correlation coefficient evaluation(rho), which were calculated using MedCalc® 22.017. 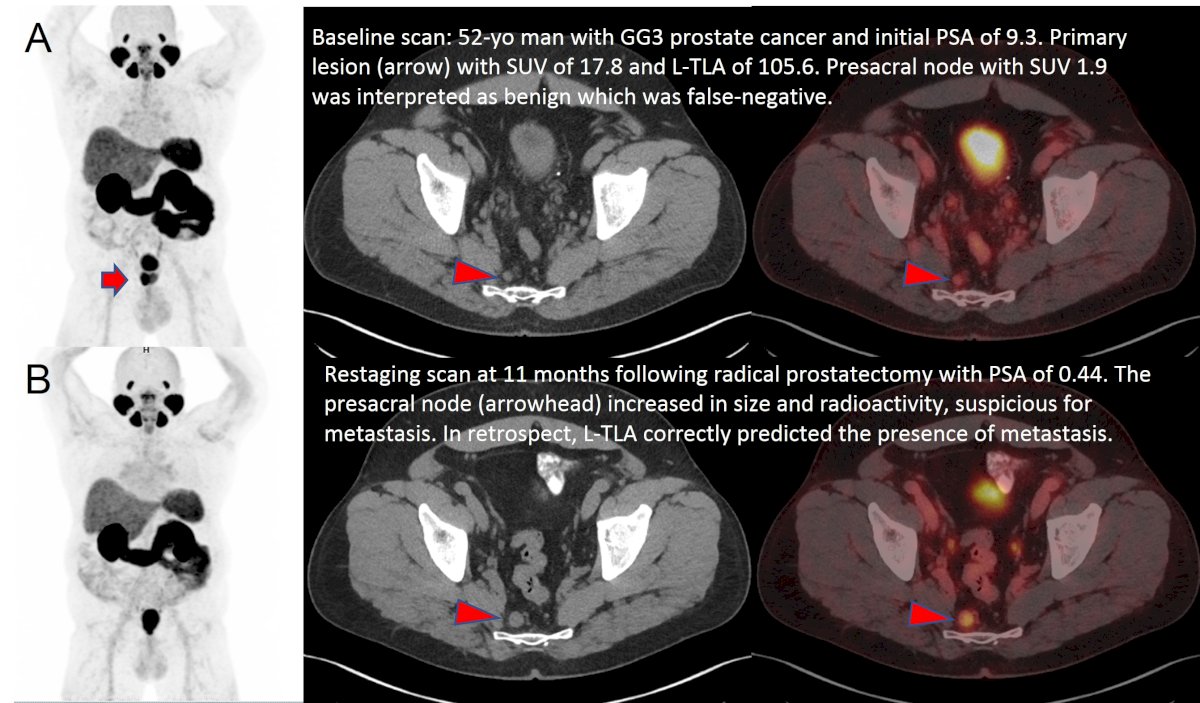
The mean patient age was 67 years. Histopathology was available for 18 subjects (26%). ROC analysis revealed that all evaluated variables, except for PSA/TP-TLA ratio, were significant predictors of the presence of advanced disease (N1 and/or M1). On a per-patient basis, an L-TLA cut-off of >32.9 was associated with a sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV of 96.6%, 50%, 32.6%, and 98.3%, respectively, for detecting advanced disease. Additionally, GG and L-TLA demonstrated the strongest positive correlation with the degree of N1 disease (1-2; 3-5; vs. >5 nodes), with rho values of 0.443 and 0.645, respectively. Both parameters were the only statistically significant variables on logistic regression analyses, with an AUC of 0.885 (95% CI 0.743 to 0.924, P <.0001). Notably, NPV was 100% in subjects with GG ≤3 and L-TLA ≤32.9.
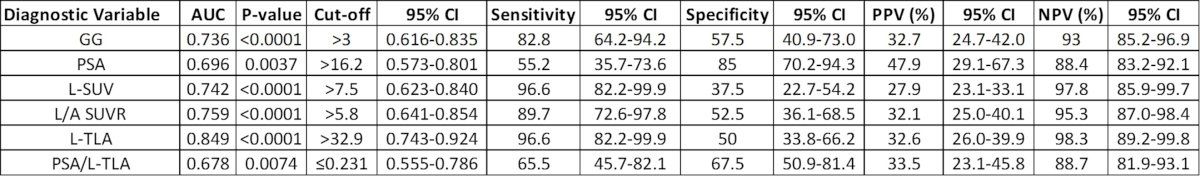
Dr. Frankl concluded that Grade Group and primary PSMA total lesion activity are the most valuable diagnostic parameters for the initial staging of patients with moderate to high-risk prostate cancer, providing a high AUC and excellent NPV, especially in subjects with Grade Group 2–3 disease and primary PSMA total lesion activity ≤32.9. Their combined use can add significant value to PET/CT interpretation. A validation study is underway to confirm these results.
Presented by: Joseph Frankl, MD, Resident Physician, Department of Radiology, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX
Written by: Rashid Sayyid, MD, MSc – Society of Urologic Oncology (SUO) Clinical Fellow at The University of Toronto, @rksayyid on Twitter during the Society of Nuclear Medicine & Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) 2024 Annual Meeting held in Toronto, ON between June 8th and June 11th, 2024
References:- Hope TA, Eiber M, Armstrong WR, et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET for Pelvic Nodal Metastasis Detection Prior to Radical Prostatectomy and Pelvic Lymph Node Dissection: A Multicenter Prospective Phase 3 Imaging Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2021;7(11): 1635-42.
- Maurer T, Gschwend JE, Rauscher I, et al. Diagnostic Efficacy of (68)Gallium-PSMA Positron Emission Tomography Compared to Conventional Imaging for Lymph Node Staging of 130 Consecutive Patients with Intermediate to High-Risk Prostate Cancer. J Urol. 2016;195(5): 1436-43.


