(UroToday.com) Androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) has been a cornerstone in the treatment of advanced prostate cancer for decades. While initially indicated for patients with metastatic disease alone, its use has expanded. Thus, while ADT has proven survival benefits, there is an increasing need to understand the costs associated with its use in the management of biochemical recurrence (BCR), metastatic hormone sensitive prostate cancer (mHSPC) and castration resistant prostate cancer (CRPC).
In a poster presentation at the Society of Urologic Oncology Annual Meeting, Dr. Demus and colleagues presented results of their work examining the relative cost of antiandrogen and ADT and to identify recent prescribing trends across these disease states.
To do so, they used the Medicare Physician & Other Practitioners and Part D Drug Databases to extract all drug claims and services made by urologists from 2013 to 2019. They then derived total drug costs in each year and nominal costs associated with the use of antiandrogens (Abiraterone Acetate, Apalutamide and Enzalutamide) and Gonadotropin-targeting agents (Leuprolide Acetate, Triptorelin Pamoate, Goserelin Acetate and Degarelix Acetate). They then estimated the cost per treatment day by dividing the ‘total drug cost’ by ‘covered treatment days’ (note: one 30-day claim is equivalent to 30 treatment days).
In total, they found that the cost of medications prescribed by urologists to MPD beneficiaries exceeded $1.6 billion in 2019. Of these, 31.4% of costs were due to antiandrogens which accounted for 0.4% of urologic drug claims. The number or urologists prescribing antiandrogens increased 13-fold during the study period from 118 urologists in 2013 to 1691 urologists in 2019. The estimated cost-per-day for patients receiving antiandrogen therapy approached $400 per-day in 2019 (ie $12,000/month or $144,000/year).

In contrast, over time, costs attributable to Gonadotropin-targeting agents increased over time from 1.4 to 1.8% of costs under Part D and 8.4 to 9.3% of costs under Part B. Notably, the preponderance of these were attributable to leuprolide. The estimated cost-per-day for ADT was $50 or less per-day under Part D and $10 or less under Part B.
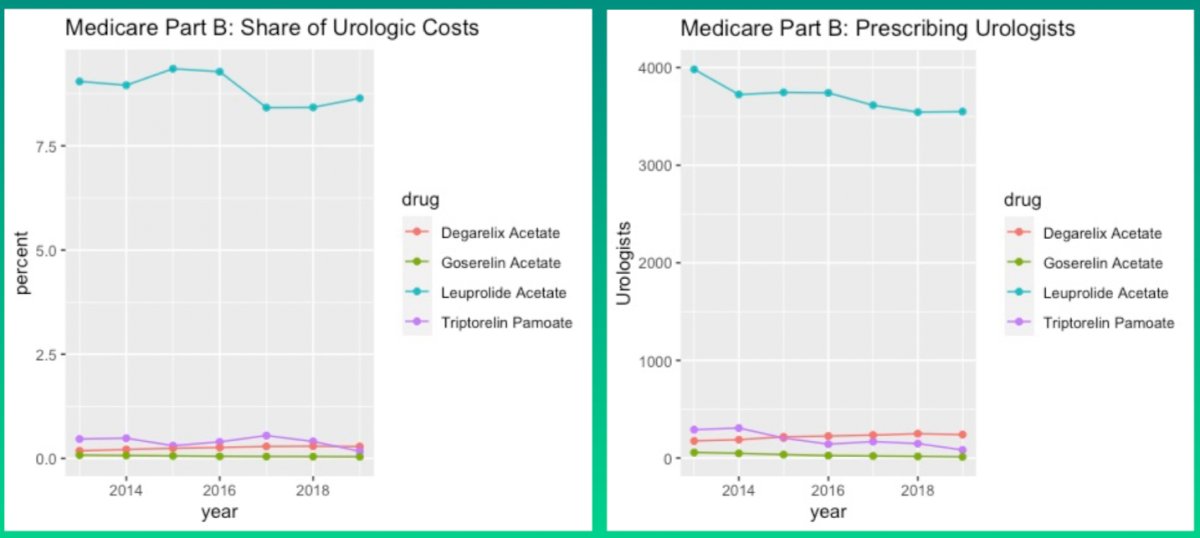
The authors conclude that, while antiandrogens account for fewer than 0.5% of all claims for medication prescribed by urologists to MPD beneficiaries, they account for nearly one-third of all costs. These are expected to increase as more physicians prescribe these novel hormonal therapies and disease indications expand.
Presented by: Timothy Demus, MSc, Columbia University Division of Urology at Mount Sinai Medical Center

