(UroToday.com) The 2023 Society of Urologic Oncology (SUO) annual meeting held in Washington, D.C. between November 28th and December 1st, 2023, was host a prostate cancer session. Dr. Rana McKay presented the NePtune trial, a phase 2 study of neoadjuvant PARP inhibition plus androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) followed by radical prostatectomy in patients with unfavorable intermediate- or high-risk prostate cancer with BRCA1/2 gene alterations
Patients with high-risk disease account for approximately 15% of localized prostate cancer.1 Significantly, despite aggressive, often multimodal definitive therapy, these patients remain at high-risk of disease recurrence and mortality.2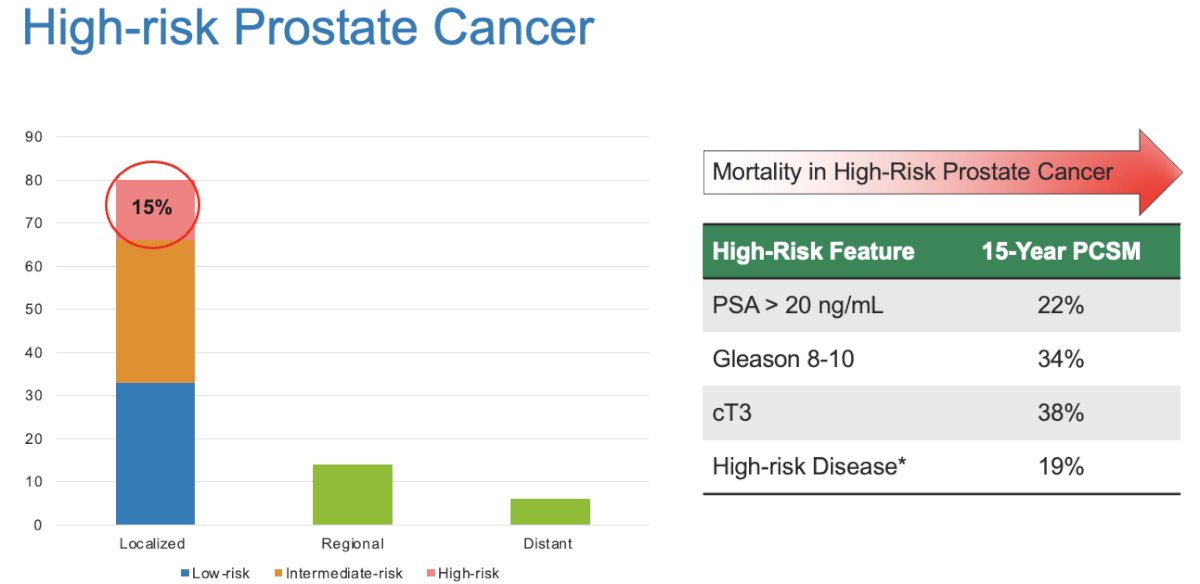
It appears that the incidence of pathogenic germline DNA repair gene mutations in patients with either Grade Group 4 disease or NCCN high-risk disease is around 6%, which is higher than that observed in patients with Grade Group 1 – 3 (4%) or NCCN low to intermediate-risk disease (2%).3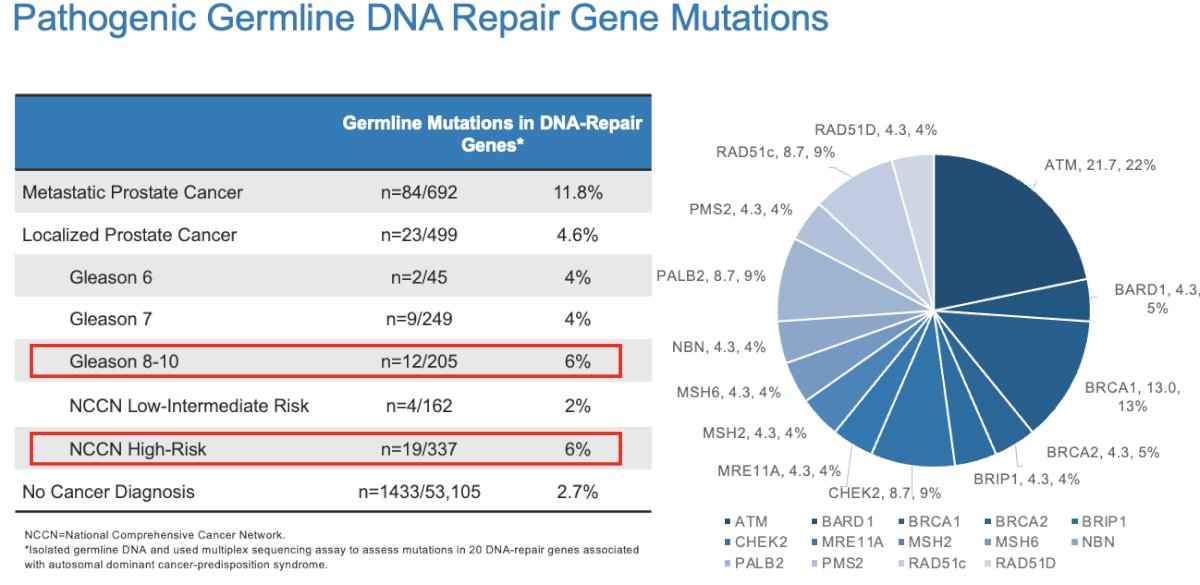
Importantly, patients with germline DNA repair gene mutations have significantly worse survival outcomes.4
Currently, the NCCN guidelines recommend germline testing for high-risk prostate cancer patients:
Given the adverse prognostic significance of these mutations in this already high-risk patient population, is there a role for targeted neoadjuvant therapy to improve outcomes? The goals of neoadjuvant treatment are to:
- Improve long-term survival with multi-modal therapy
- Current standard of care for breast, rectal, bladder, and other cancers
- Downstage locally advanced disease, which may facilitate surgical resection and reduce post-operative morbidity
- Reduce or delay the morbidity from post-radical prostatectomy therapies such as salvage radiotherapy and ADT
- Provide in vivo assessment of response to treatment and a platform to evaluate pharmacodynamic endpoints
It has been demonstrated in multiple other disease sites that pathologic response is prognostic of outcomes in:
- Bladder cancer (Petrelli et al, Eur Urology, 2014)
- Esophageal cancer (Berger et al, JCO, 2005)
- Rectal cancer (Mass et al, Lancet Oncology, 2010)
- Breast cancer (Cortazar et al, Lancet Oncology, 2014)
As such, the FDA has recommended pathologic complete response as an endpoint for accelerated approval of new agents for neoadjuvant treatment of high-risk early breast cancer, as an example.5
There have been numerous studies of neoadjuvant therapy in the high-risk, localized prostate cancer setting, with some examples summarized in the table below. However, to date, none of these trials have culminated in any practice-changing results, and neoadjuvant therapy remains non-standard of care outside of a clinical trial setting. As highlighted below, the composite outcome of pathologic complete response or minimal residual disease has ranged between 17% and 30%, although the recently reported ACDC-RP trial reported a composite pathologic response of approximately 44%.6 And while there is some evidence that improved pathologic responses correlate with improved biochemical survival outcomes, there remains an ongoing effort to improve upon these historical rates.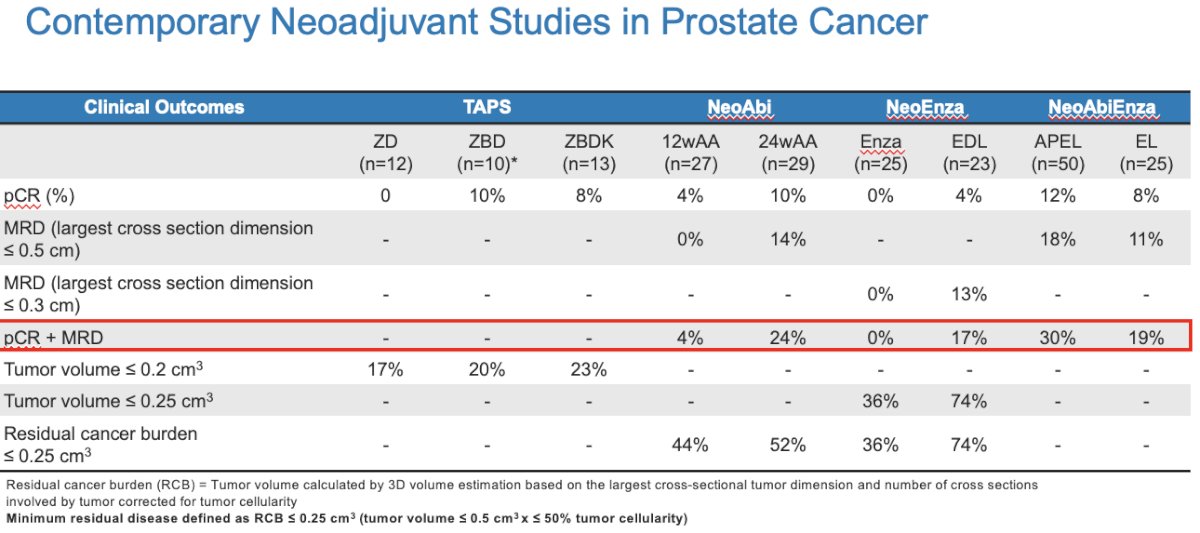
What about long-term outcomes from these trials? In a pooled analysis of three neoadjuvant trials of ‘intense’ ADT, McKay et al. demonstrated that the 3-year biochemical recurrence-free rate was 70%. Of the 15 patients with either residual tumor ≤ 0.5 cm or pathologic T downstaging, no patient experienced a recurrence during the 3.4-year median follow-up.7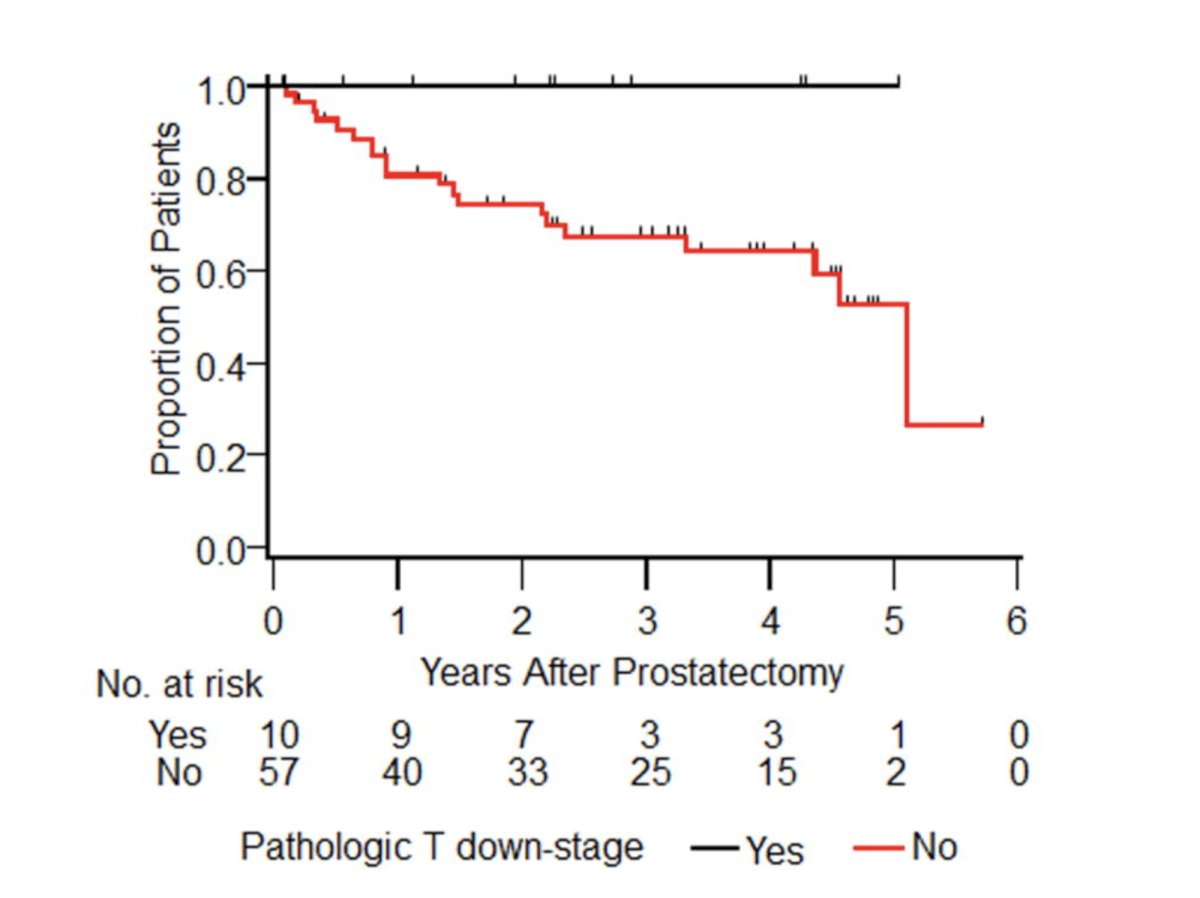
Over the last few years, we have witnessed the emergence of numerous biomarker-driven trials in the high-risk localized prostate cancer setting. We eagerly await the results of the Genomic Umbrella Neoadjuvant Study (GUNS) trial (NCT04812366), which is an adaptive, multi-arm, multi-stage trial designed to evaluate targeted therapies in biomarker-pre-selected patients with high-risk localized disease by matching neoadjuvant therapies to baseline genomic alterations.
Recently, a trial of neoadjuvant talazoparib in patients with ≥1 cm invasive breast cancer with germline BRCA-positive disease and operable breast cancer demonstrated that over half (53%) had a pathologic complete response, with an additional 10% having minimal residual disease.8 As such, Dr. McKay argued that these results provide an analogous paradigm to investigate PARP inhibitors pre-operatively in patients with germline BRCA mutations.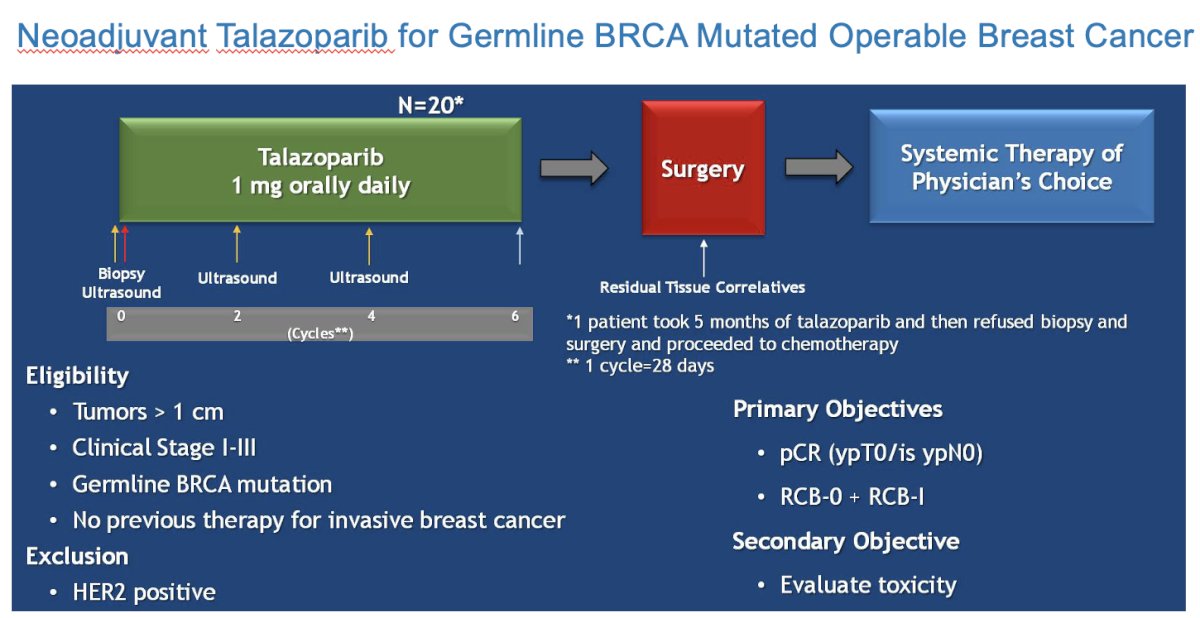
The NePtune trial (NCT05498272) is evaluating neoadjuvant PARP inhibition + ADT followed by radical prostatectomy in patients with unfavorable intermediate- or high-risk prostate cancer with BRCA1/2 gene alterations. This will include patients meeting the following eligibility criteria:
- Gleason ≥ 4+3 (grade group 3, 4, 5) OR
- PSA > 20 ng/dL
OR
- T3 disease
- PLUS
- Pathogenic or likely pathogenic germline or somatic BRCA1/2 gene alteration on chemiluminescent immunoassay (CLIA)-based assay
- Pelvic adenopathy ≤ 2 cm
Patients will receive olaparib + an LHRH agonist for 6 months, following which they will undergo a radical prostatectomy. The primary endpoint is pathologic complete response or minimal residual disease. Secondary objectives including the following:
- Compare changes in PSA
- Evaluate surgical pathologic outcomes at radical prostatectomy
- Evaluate residual cancer burden at radical prostatectomy
- Evaluate event-free survival
- Evaluate treatment-free survival (including adjuvant or salvage radiation therapy, ADT, or other therapies) post-radical prostatectomy
- Correlate pathologic response (pathologic complete response and/or minimal residual disease) with biochemical progression free survival
- Evaluate time to testosterone recovery post-radical prostatectomy
- Evaluate safety and tolerability of therapy
- Evaluate intra- and post-operative complications
- Evaluate cardiovascular adverse events
Dr. McKay concluded her presentation of NePtune as follows:
- Patients with germline/somatic BRCA1/2 alterations have inferior outcomes
- PARP inhibitors have demonstrated efficacy in prostate cancer with BRCA1/2 alterations
- The NePtune trial is testing neoadjuvant olaparib plus ADT followed by radical prostatectomy for patients with unfavorable-intermediate or high-risk prostate cancer with somatic/germline BRCA1/2 alterations
Presented by: Rana McKay, MD, Associate Professor, Department of Medicine, University of California, San Diego, CA
Written by: Rashid K. Sayyid, MD, MSc – Society of Urologic Oncology (SUO) Clinical Fellow at The University of Toronto, @rksayyid on Twitter during the 2023 Society of Urologic Oncology (SUO) annual meeting held in Washington, D.C. between November 28th and December 1st, 2023
References:- Cooperberg MR, Broering JM, Carroll PR. Time trends and local variation in primary treatment of localized prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2020;28(7):1117-1123.
- Eggener SE, Scardino PT, Walsh PC, et al. Predicting 15-year prostate cancer specific mortality after radical prostatectomy. J Urol. 2011;185(3):869-875.
- Prtichard CC, Mateo J, Walsh MF, et al. Inherited DNA-Repair Gene Mutations in Men with Metastatic Prostate Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:443-453.
- Castro E, Goh C, Olmos D, et al. Germline BRCA mutations are associated with higher risk of nodal involvement, distant metastasis, and poor survival outcomes in prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(14):1748-1757.
- Bossuyt V, Provenzano E, Symmans WF, et al. Recommendations for standardized pathological characterization of residual disease for neoadjuvant clinical trials of breast cancer by the BIG-NABCG collaboration. Ann Oncol. 2015;26(7):1280-1291.
- Fleshner NE, Sayyid RK, Hansen AR, et al. Neoadjuvant Cabazitaxel plus Abiraterone/Leuprolide Acetate in Patients with High-Risk Prostate Cancer: ACDC-RP Phase II Trial. Clin Cancer Res. 2023;29(19):3867-3874.
- McKay RR, Montgomery B, Xie W, et al. Post prostatectomy outcomes of patients with high-risk prostate cancer treated with neoadjuvant androgen blockade. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2018;21(3):364-372.
- Litton JK, Scoggins ME, Hess KR, et al. Neoadjuvant Talazoparib for Patients With Operable Breast Cancer With a Germline BRCA Pathogenic Variant. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(5):388-394.


