(UroToday.com) The 2024 SUO annual meeting included a kidney cancer session, featuring a presentation by Dr. Eric Jonasch discussing a phase 1B/2 study of combination 177Lu Girentuximab + cabozantinib and nivolumab in treatment naïve patients with advanced clear cell RCC. To date, complete response is a rare event advanced clear cell RCC.
The combination of nivolumab plus cabozantinib was recently approved for first-line treatment of clear cell RCC, demonstrating improved progression-free survival and objective response rate in comparison to sunitinib.1 However, complete response is only 9%.
The anti-tumor effects of immune checkpoint inhibitors are dependent on activated tumor infiltrating T cells. Thus, drugs that could synergize with T cell anti-tumor activity can improve complete response rates. Radiation-induced DNA damage to activate the cGAS-STING pathway is a promising mechanism, and many studies have shown that radiation treatment augments immune checkpoint inhibition. However, it is not always possible to radiate all metastatic lesions. Targeted peptide receptor radionuclide therapies have been developed by conjugating radioisotopes to receptor binding analogs, targeting specific cancer cell surface proteins, thereby delivering targeted radiation to cancer cells in the body with minimal damage to surrounding healthy cells:
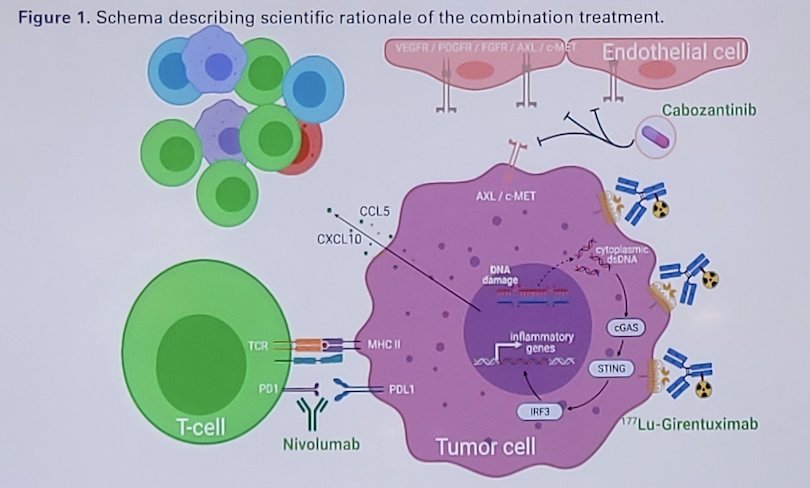
177Lu-girentuximab is the first antibody-radioisotope designed for clear cell RCC, targeting carbonic anhydrase IX-expressing cells expressed in >90% clear cell RCC to deliver targeted radiation to cancer with minimal damage to surrounding healthy cells. As a single agent in metastatic clear cell RCC, 177Lu-girentuximab was safe and effective in stabilizing disease in 57% of patients.2 Dr. Jonasch and colleagues hypothesize that 177Lu-girentuximab-induced DNA damage will potentiate the STING pathway, synergizing with nivolumab and cabozantinib to promote trafficking and infiltration of activated T cells and achieve higher complete response rates.
This single arm phase 1b/2 study will test the hypothesis that adding 177Lu-girentuximab to cabozantinib and nivolumab will increase the complete response rate when compared to historical outcomes with nivolumab + cabozantinib. The primary objective is to determine the safety and complete response rate of this treatment option in previously untreated clear cell RCC patients. 177Lu-girentuximab 1480 MBq/m2 (61% of single agent maximum tolerated dose) will be administered every 12 weeks for up to 3 cycles. Starting with the second cycle, nivolumab, and cabozantinib will be added at standard dose: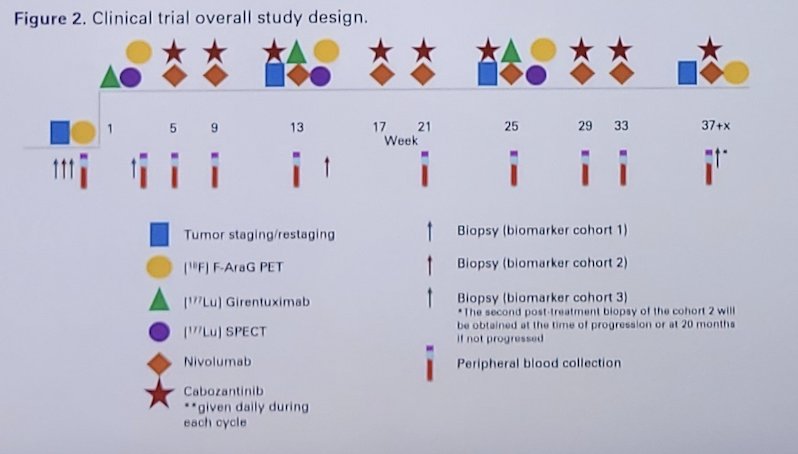
Up to 100 patients with treatment naive, biopsy-proven clear cell RCC with adequate organ/marrow function with 1 evaluable lesion by RECIST 1.1 will be enrolled. A 5 patient safety lead-in will evaluate myelosuppression. Ongoing safety and futility monitoring will employ a Bayesian approach. The sample size was chosen for reasonable operating characteristics to distinguish a complete response rate (primary endpoint) of 18% as better than 9% using a beta (0.09, 0.91) prior. Secondary endpoints are objective response rate, progression free survival by RECIST 1.1, and overall survival. To explore the effects of the treatment on inducing activated T cell infiltration, patients will undergo pre/post-treatment PET scan with 18F-AraG radiotracer as well as biopsies for single cell, spatial transcriptomics, and proteomics studies.
Presented by: Eric Jonasch, MD, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX
Written by: Zachary Klaassen, MD, MSc – Urologic Oncologist, Associate Professor of Urology, Georgia Cancer Center, Wellstar MCG Health, @zklaassen_md on Twitter during the 2024 Society of Urologic Oncology (SUO) Annual Meeting, Dallas, TX, Tues, Dec 3 – Fri, Dec 6, 2024.
References:
- Choueiri TK, Powles T, Burotto M, et al. Nivolumab plus cabozantinib versus sunitinib for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2021 Mar 4;384(9):829-841.
- Muselaers CJH, Boers-Sonderen MJ, van Oostenbrugge TJ, et al. Phase 2 Study of Lutetium 177–Labeled Anti–Carbonic Anhydrase IX Monoclonal Antibody Girentuximab in Patients with Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma. Eur Urol. 2016 May;69(5):767-770.


