(UroToday.com) The 2024 Society of Urologic Oncology (SUO) annual meeting held in Dallas, between December 3 and December 6, 2024, was host to the Kidney Cancer Session II. Dr Naomi Haas presented an update on Neoadjuvant therapy trials in renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
Dr. Haas began her presentation by noting that recently completed trials in the neoadjuvant space have demonstrated safety, but with limited evidence of pathologic response or RECIST partial response. She highlighted five trials in this setting, which explored different combinations of immune checkpoint inhibitors (IO) and targeted therapies (TKIs), IO-IO combinations, and even IO monotherapy. A comprehensive summary of the drugs evaluated, duration of therapy, and preliminary results is outlined below.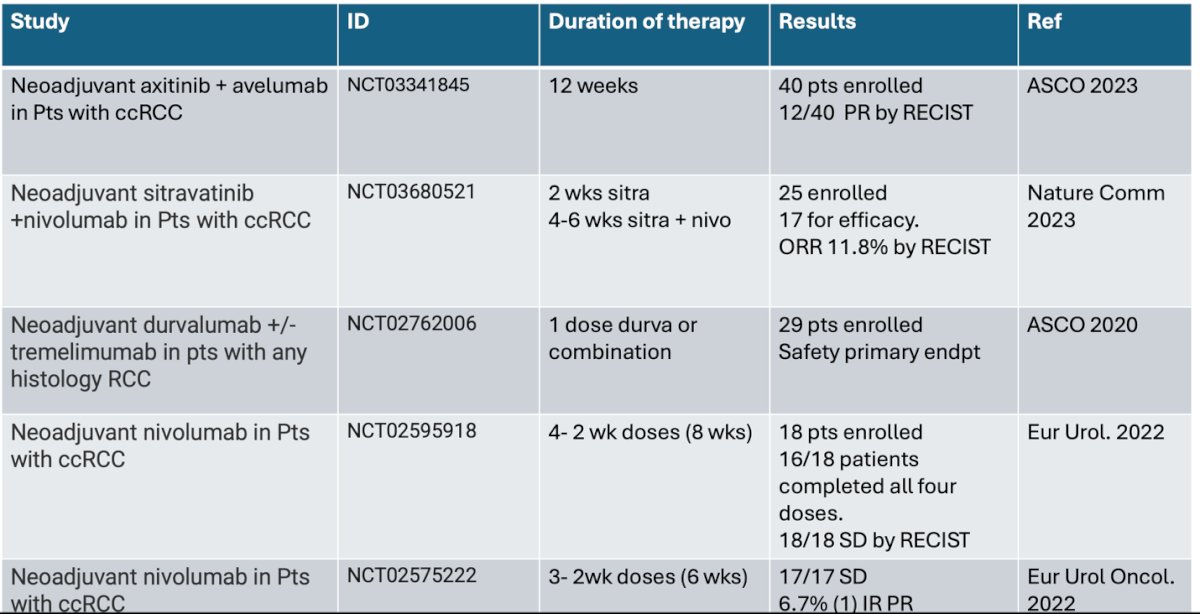
She moved on to discuss the PROSPER-RCC study. For PROSPER, entry criteria included patients with clinical stage ≥T2 or T any N+ RCC planned for nephrectomy (partial or radical). Select oligometastatic disease was permitted if the patient could be rendered ‘no evidence of disease’ (NED) within 12 weeks of surgery. In the investigational arm, nivolumab was administered (480mg IV q4 weeks) with 1 dose prior to surgery followed by 9 adjuvant doses. The control arm was surgery followed by surveillance without a placebo. Baseline tumor biopsy was required only in the nivolumab arm. The trial schema for PROSPER is as follows:
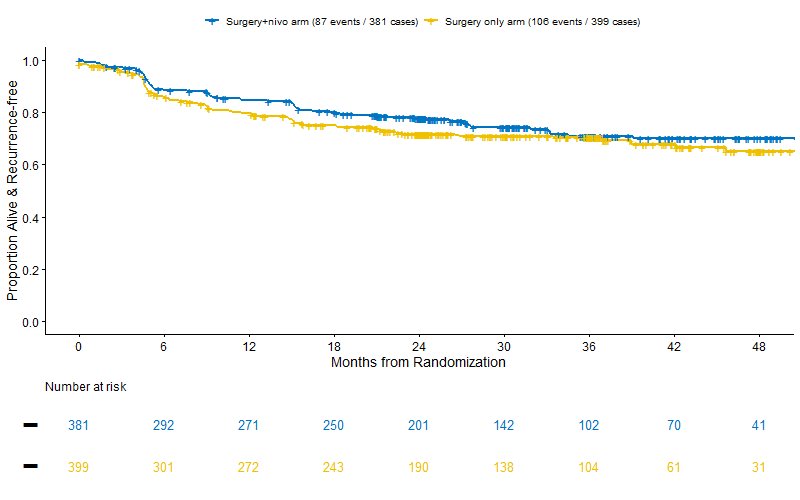
PROSPER enrolled 819 patients, randomized to perioperative nivolumab (n = 404) or surgery alone (n = 415), at the interim analysis, the data safety monitoring committee stopped the trial early due to futility (stratified hazard ratio for RFS exceeded a threshold of 0.96). At a median follow-up of 16 months, RFS was similar between the arms (HR 0.97, 95% CI 0.74 – 1.28; p= 0.43), and the median RFS was not reached.1
However, in a prespecified recurrence-free survival sensitivity analysis, patients who did not undergo surgery or were not disease-free after surgery were censored at day 1, rather than being counted as an event on day 1. The nivolumab plus surgery group had fewer recurrences than the surgery-only group (20% vs. 24%), but no significant difference between the groups was found (p=0.07).
There are multiple ongoing ICI + VEGFR-TKI trials testing different durations of treatment. To highlight some of them: one trial is testing neoadjuvant lenvatinib + pembrolizumab in patients with IVC thrombus, receiving 12 weeks of neoadjuvant therapy. Another trial is testing the same combination in patients with RCC, but with only 3 weeks of neoadjuvant therapy. These patients then go on to a sandwich therapy with adjuvant pembrolizumab. A comprehensive summary of these ongoing trials is shown below.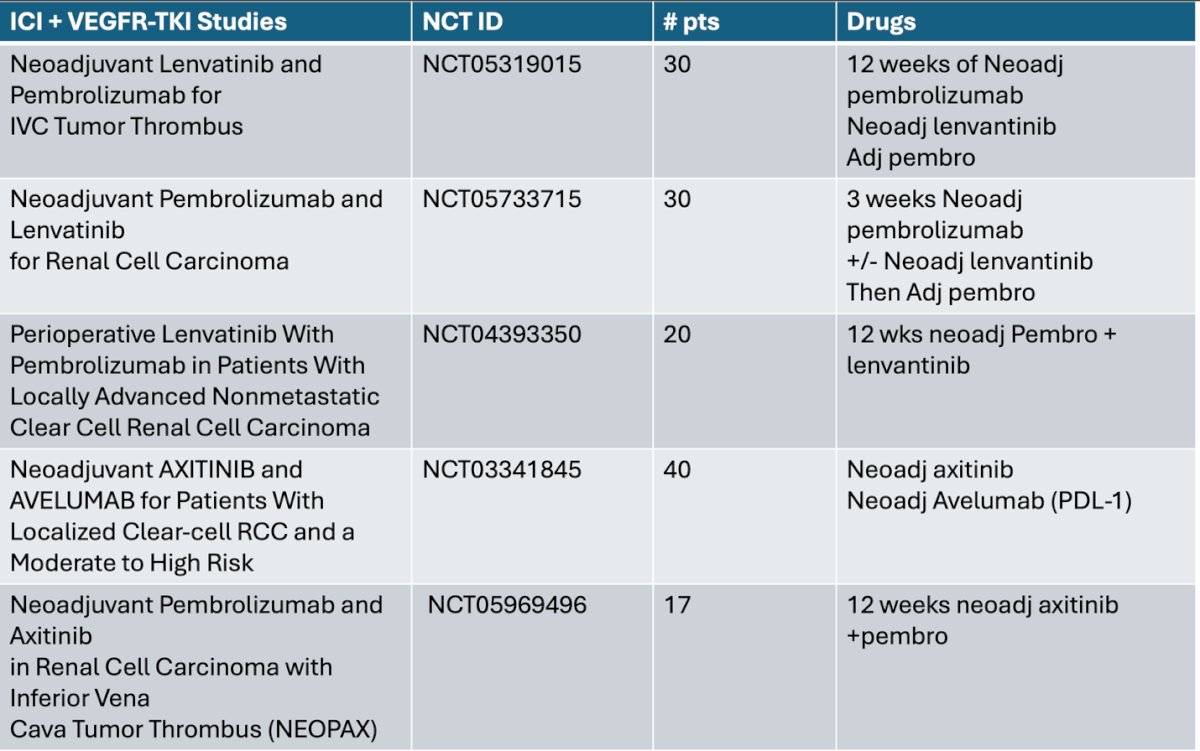
There are three ongoing ICI Trials testing optimal perturbation of the tumor immune system and rate of pathologic response, this are the NESCIO trial, the SPARC-1 and NAPSTER.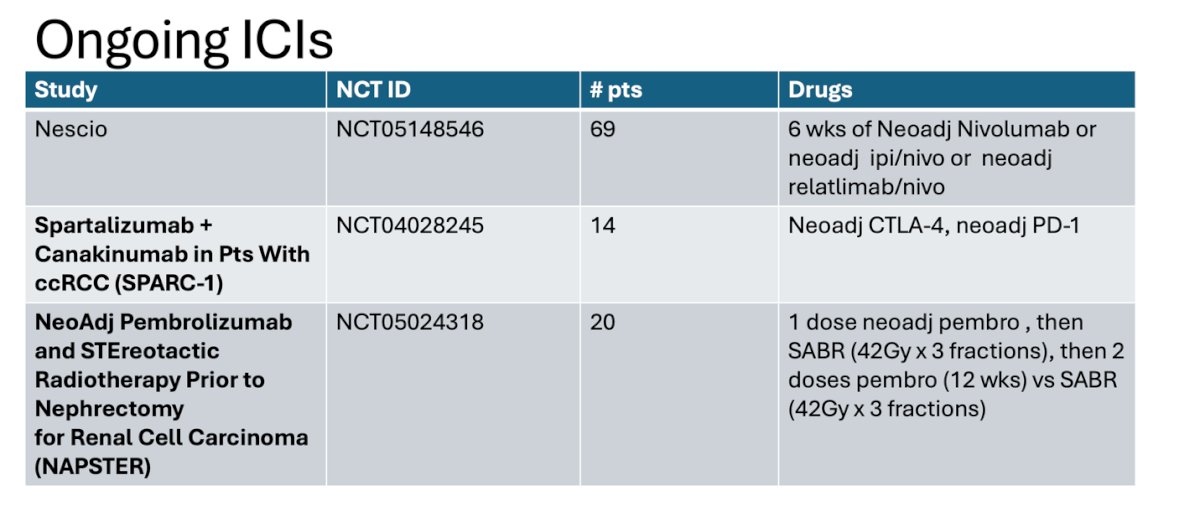
The NESCIO trial enrolled patients with clear cell RCC and intermediate-high risk M0 and randomized them into three arms: nivolumab, nivolumab + ipilimumab, and nivolumab + relatlimab, all followed by nephrectomy. The primary endpoint is the pathologic response rate (complete or partial pathologic response). Secondary endpoints include safety and feasibility, objective response rate, EFS, RFS, rate of distant metastases, local recurrence at 5 years after the start of treatment, and surgical morbidity according to the Clavien-Dindo classification. The study design is shown below.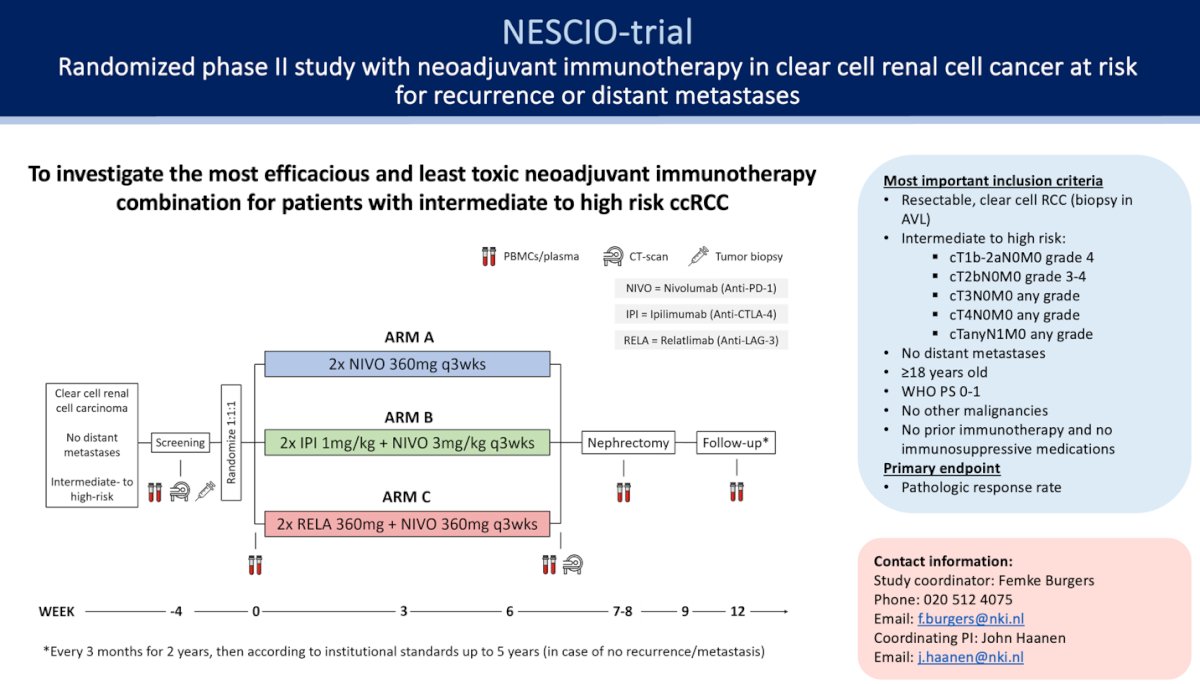
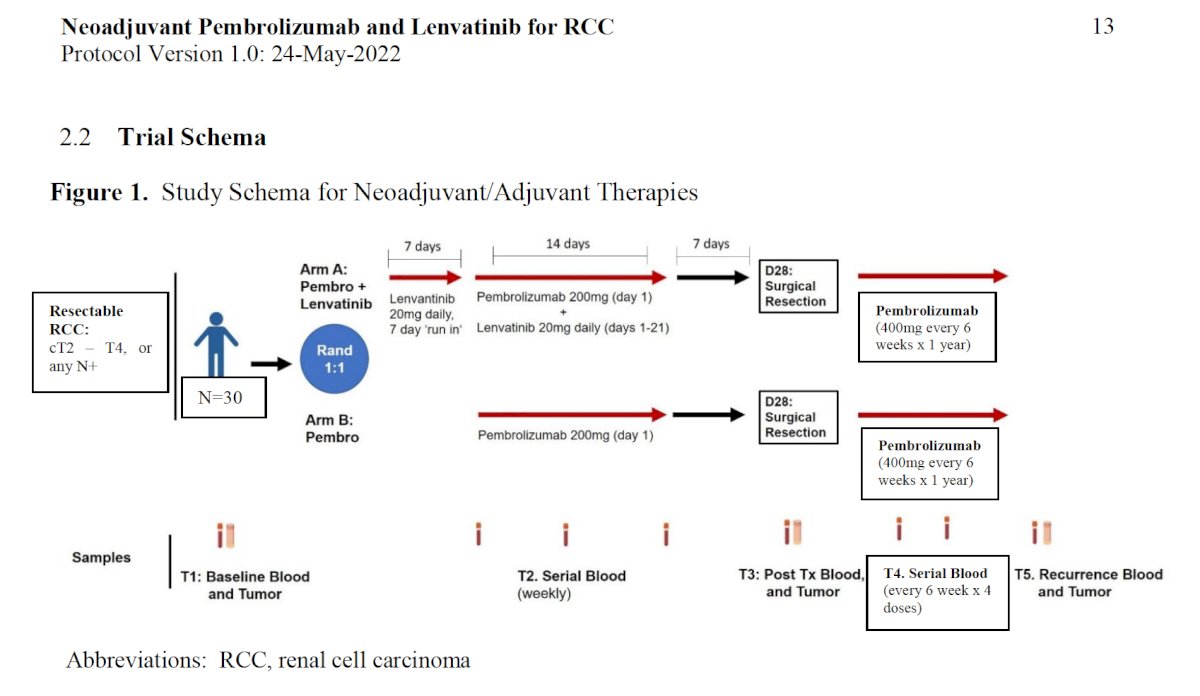
Another interesting combination in the neoadjuvant setting is neoadjuvant pembrolizumab + lenvatinib for RCC. The study enrolled patients with resectable RCC (cT2-4, any N+) and randomized them 1:1 to either lenvatinib + pembrolizumab with surgical resection at Day 28, followed by adjuvant pembrolizumab for 1 year, or pembrolizumab alone followed by surgery and adjuvant pembrolizumab for 1 year. Results are eagerly awaited.
Dr. Haas pivoted on to trials that about to launch and being proposed including
- Neoshift (placeholder)
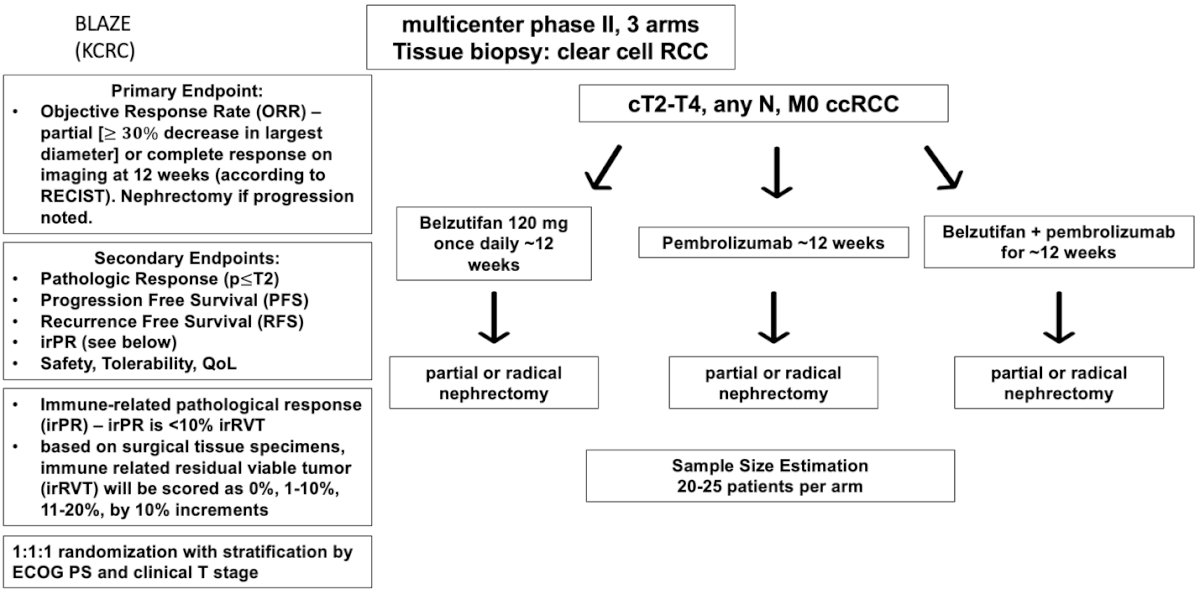
- Blaze (trial design illustrated below)
However, many questions remain to be answered, such as: What is the ideal duration of therapy? Is 12 weeks necessary, or could a shorter duration (e.g., 3 weeks) be sufficient? Which is the right combination: dual IO, TKI+IO, HIF+IO? And what is the ideal primary endpoint? Hopefully, all these ongoing trials will help us answer these questions in the not so distant future.
A promising biomarker for RCC is Kidney Injury Molecule-1 (KIM-1), a type 1 membrane glycoprotein identified as a marker for unresected clear cell RCC and early detection of RCC. In a study presented at ASCO 2024, patients treated in the IMmotion 010 study showed that KIM-1–high status was associated with reduced disease-free survival. However, patients with high KIM-1 had better disease-free survival when treated with atezolizumab compared to placebo (HR 1.75, 95% CI 1.40-2.17). 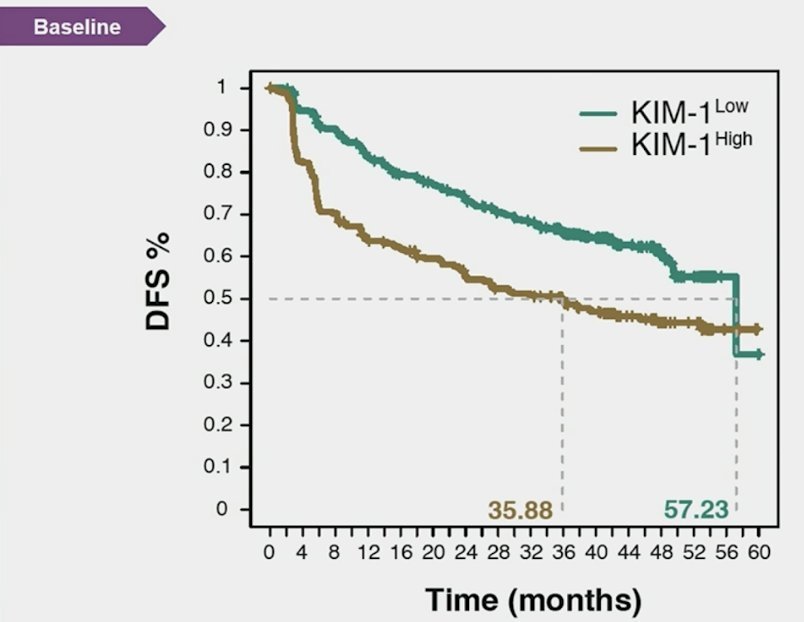
Similarly, in the CheckMate-914 study, patients in the arm receiving nivolumab + ipilimumab with high KIM-1 levels were associated with worse disease-free survival (DFS). However, these patients showed potential benefit from adjuvant nivolumab + ipilimumab. This highlights the potential of using KIM-1 as a biomarker in designing future trials.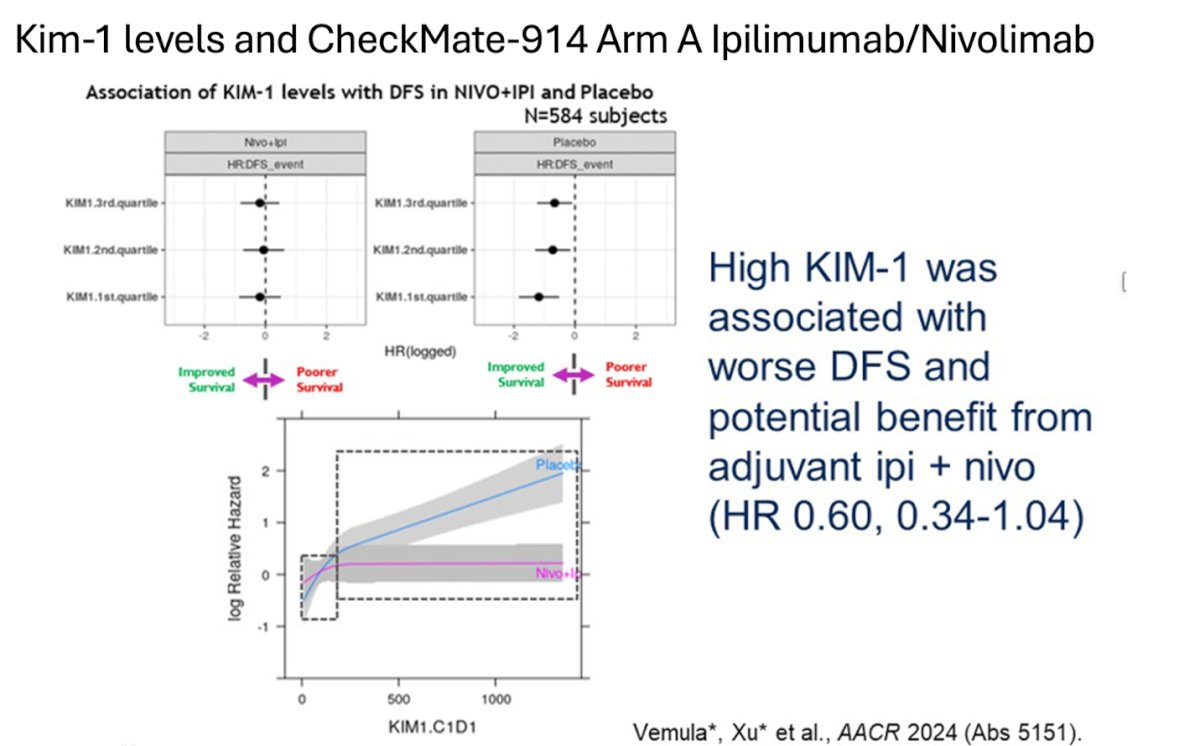
Dr. Haas shared the ideal future trial design in the neoadjuvant setting and summarized it in a comprehensive algorithm below.
Dr. Haas concluded her presentation with the following take home messages:
- Phase 2 IO’s and PROSPER trial showed no additional surgical risks or delay to surgery after perioperative immunotherapy.
- VEGFR-TKI +IO shows more shrinkage but not necessarily increased pathologic response
- Only phase 3 (PROSPER) conducted tested 1 dose of nivolumab followed by surgery and 9 months nivolumab and was (−) for DFS but this trial had several limitations:
- Included non-clear cell RCC
- No adjuvant arm
- 1 dose Nivolumab only
- 11% pT1, 21% pT2 Placebo arm (N=415)
- The Neoadjuvant strategy is proven in another IO-sensitive cancers: Melanoma (NADINA), NSCLC
Presented by: Naomi Haas, MD, Medical Oncologist, Professor of Medicine (Hematology-Oncology) at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania.
Written by: Julian Chavarriaga, MD – Urologic Oncologist at Cancer Treatment and Research Center (CTIC) Luis Carlos Sarmiento Angulo Foundation via Society of Urologic Oncology (SUO) Fellow at The University of Toronto. @chavarriagaj on Twitter during the 2024 Society of Urologic Oncology (SUO) annual meeting held in Dallas, between the 3rd and 6th of December, 2024.
References:

