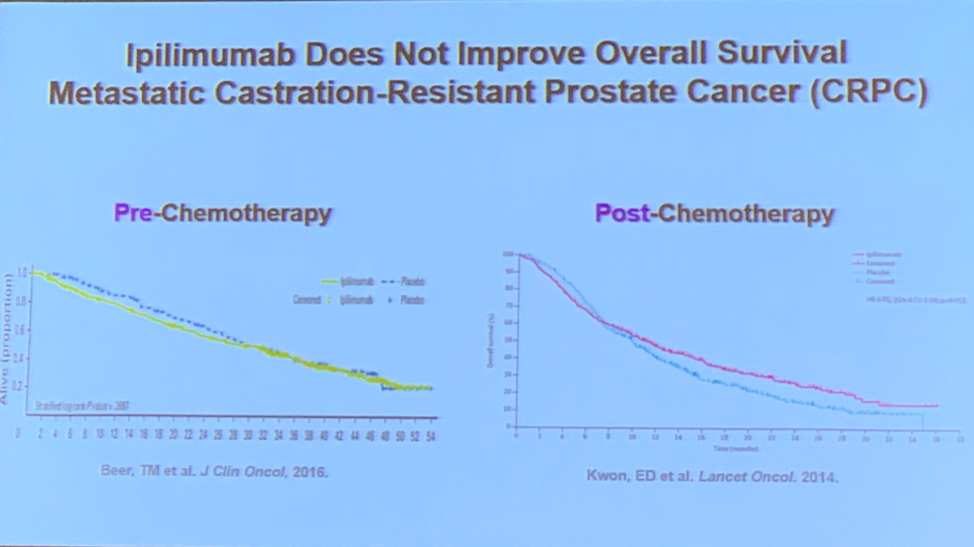
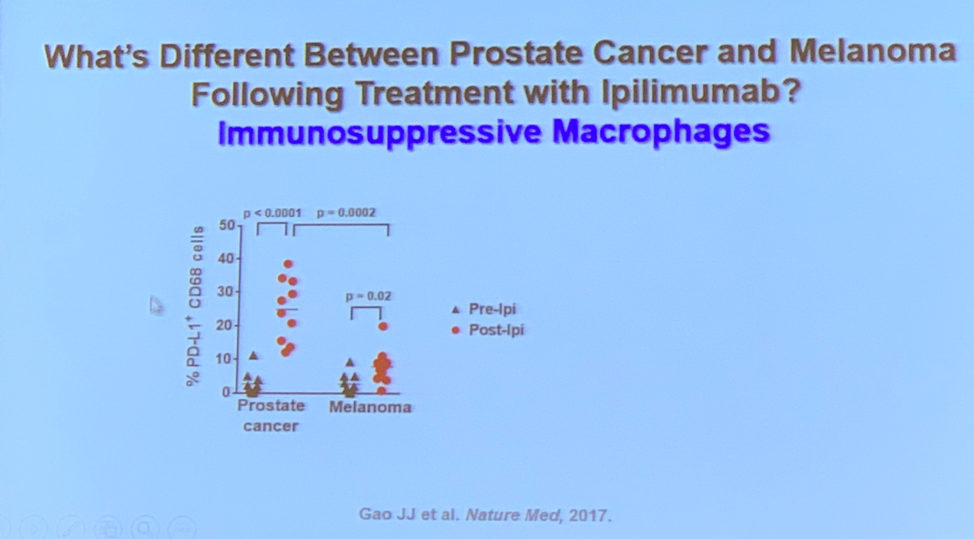
The more recent class of immunotherapies, immune checkpoint inhibitors, also have a role in the treatment of prostate cancer. The early studies of ipilimumab, a drug with good results in several other cancers (e.g. melanoma), failed to demonstrate a survival benefit1,2. Dr. Subudhi’s research has determined that despite the recruitment of ample immune cells to the tumor tissue by ipilimumab the macrophages detected in the tumor microenvironment exhibit a resistance mechanism. Work is ongoing in their laboratory to determine how and why the resistance occurs. They have identified a candidate cell surface marker, VISTA, that is upregulated in prostate cancer tumors on both cancer cells and immune cells3.
Presented by: Sumit K. Subudhi, MD, Department of Genitourinary Medical Oncology, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX, USA
Written by Justin T. Matulay, MD, Urologic Oncology Fellow and Ashish M. Kamat, MD (@UroDocAsh), Professor, Department of Urology, Division of Surgery, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX at the 13th Update on the Management of Genitourinary Malignancies, The University of Texas (MDACC - MD Anderson Cancer Center) November 9-10, 2018, Dan L. Duncan Building, Houston, TX
References:
1. Beer, T.M., E.D. Kwon, C.G. Drake, et al., Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase III Trial of Ipilimumab Versus Placebo in Asymptomatic or Minimally Symptomatic Patients With Metastatic Chemotherapy-Naive Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. J Clin Oncol, 2017. 35(1): p. 40-47.
2. Kwon, E.D., C.G. Drake, H.I. Scher, et al., Ipilimumab versus placebo after radiotherapy in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer that had progressed after docetaxel chemotherapy (CA184-043): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol, 2014. 15(7): p. 700-12.
3. Gao, J., J.F. Ward, C.A. Pettaway, et al., VISTA is an inhibitory immune checkpoint that is increased after ipilimumab therapy in patients with prostate cancer. Nat Med, 2017. 23(5): p. 551-555.


