Table 1. Characteristics of the Selected Trials
| KEYNOTE-564 | IMmotion 010 | PROSPER | CheckMate 914 | |
|
N |
994 |
778 |
819 |
816 |
|
Population |
pT2 G4, pT 3 Gany, pT 1 Gany pN1 or pT 1 Gany pNany M1 NED |
pT2 G4, pT 3a G 3, pT 3b Gany, pT 1 Gany pN1 or pT 1 Gany pNany M1 NED |
pT 2 Gany, pT 1 Gany N1 or pT 1 Gany pNany M1 NED |
pT2a G 3, pT 2b Gany or pTany Gany pN1 |
|
Experimental Arm |
Pembrolizumab |
Atezolizumab |
Nivolumab (neo-adjuvant and adjuvant) |
Nivolumab + Ipilimumab |
|
Control Arm |
Placebo |
Placebo |
Observation |
Placebo |
|
Duration of Treatment (mo) |
12 (17 cycles) |
12 (16 cycles) |
12 (1+9 cycles) |
6 (4 cycles of Ipi + 12 cycles of Nivo) |
|
UISS1 intermediate-high risk (%) |
86 |
62 |
NI2 |
43 |
|
UISS high risk (%) |
8 |
24 |
NI |
56 |
|
N+ (%) |
6 |
11 |
17 |
NI |
|
M1 Ressected (NED3) (%) |
6 |
14 |
3 |
None |
|
Non-Clear Cell RCC (%) |
None |
7 |
17 |
NI |
|
Sarcomatoid Component (%) |
10 |
9 |
NI |
5 |
|
PD-L1 positive (%) |
74 |
59 |
NI |
NI |
Therefore, we perform a systematic review and study-level meta-analysis including the four RCT addressing ICI in adjuvant settings totalizing 3,405 patients with localized renal cell carcinoma. In resume, for ITT population there was no DFS benefit with adjuvant ICI therapy (Figure 1). Considering the high heterogeneity associated with this analysis, subgroup analyses were performed. Thus, there were DFS benefits for PD-L1 positive and intermediate-high risk patients and patients with sarcomatoid component (Figure 2, 3 and 4, respectively).
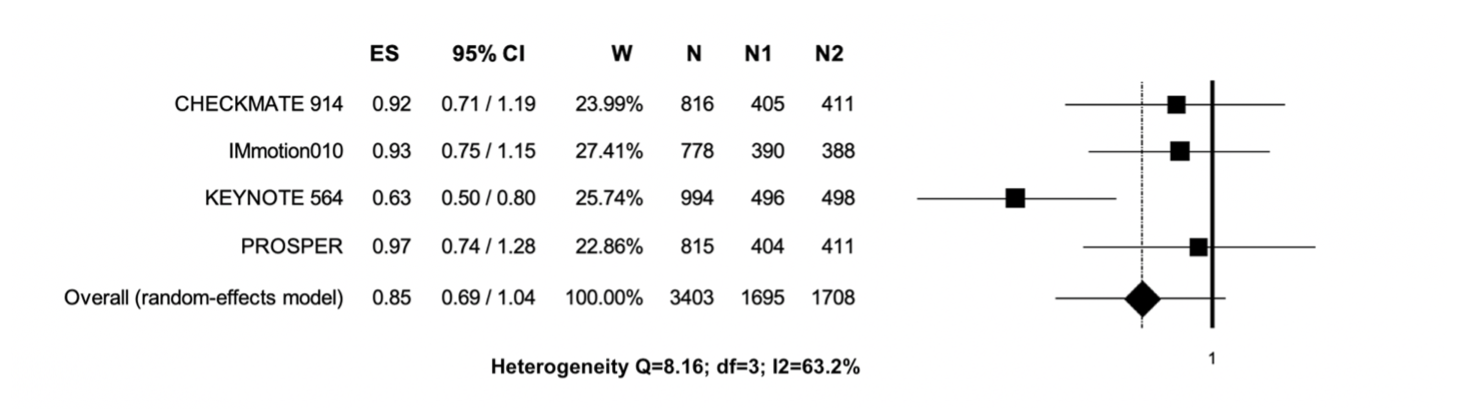
Figure 1. Adjuvant immunotherapy versus placebo / observation in the ITT population; the outcome (Effect Size) was Hazard Ratio (HR) of Disease-Free Survival (DFS). Abbreviations: CI: confidence interval; ES: Effect Size; N: total number of patients; N1: number of patients in the experimental arm; N2: number of patients in the control arm; W: weight.

Figure 2. Adjuvant immunotherapy versus placebo/observation in PD-L1 positive population; the outcome (Effect Size) was Hazard Ratio (HR) of Disease-Free Survival (DFS). Abbreviations: CI: confidence interval; ES: Effect Size; N: total number of patients; N1: number of patients in the experimental arm; N2: number of patients in the control arm; W: weight

Figure 3. Adjuvant immunotherapy versus placebo/observation in intermediate-high risk RCC patients; the outcome (Effect Size) was Hazard Ratio (HR) of Disease-Free Survival (DFS). Abbreviations: CI: confidence interval; ES: Effect Size; N: total number of patients; N1: number of patients in the experimental arm; N2: number of patients in the control arm; W: weight.
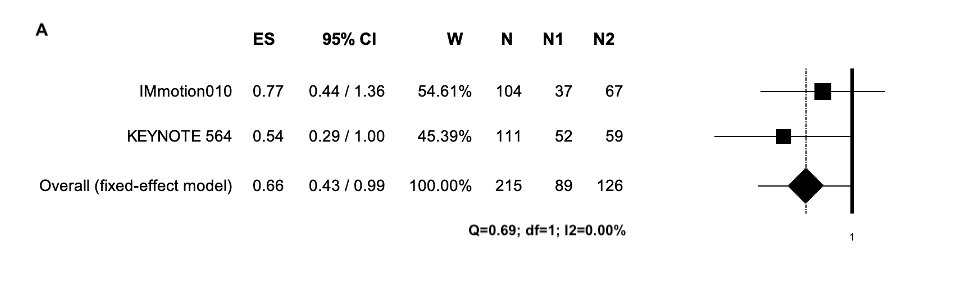
Figure 4. Adjuvant immunotherapy versus placebo in (A) patients with sarcomatoid component; the outcome (Effect Size) was Hazard Ratio (HR) of Disease-Free Survival (DFS). Abbreviations: CI: confidence interval; ES: Effect Size; N: total number of patients; N1: number of patients in the experimental arm; N2: number of patients in the control arm; W: weight.
In conclusion, considering the heterogeneity between the trials such as different populations and ICI used as well as the design of the trials and duration of ICI treatment, our meta-analysis was unable to demonstrate DFS benefit in overall population, therefore the decision to use adjuvant ICI should be individualized.
Written by: Fernando Sabino Marques Monteiro, Latin American Oncology Group (LACOG) – Genito-Urinary Tumors Section. Hospital Santa Lucia – Oncology and Hematology Department, Brazil
Read the Abstract


