The VISION trial is an international, randomized, open-label phase III study evaluating 177Lu-PSMA-617 in men with PSMA-positive mCRPC who had previously received treatment with next-generation androgen receptor signaling inhibition (abiraterone, enzalutamide, etc) and one or two prior lines of taxane chemotherapy. Additionally, patients must have had an ECOG performance status of 0-2 and a life expectancy of at least 6 months. Importantly, patients must have had PSMA-positive disease on the basis of a central review of 68Ga-PSMA-11 staging scans. PSMA positivity was defined as uptake greater in metastatic lesions than in the liver. Further, they could have no PSMA-negative metastatic lesions.
Following enrollment, patients were randomized in a 2:1 fashion to receive either 177Lu-PSMA-617 (7.4 GBq every 6 weeks x 6 cycles) plus standard of care (SOC) or SOC alone. SOC treatments were at the discretion of the treating investigator; however, cytotoxic chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and radium-223 were explicitly excluded. Most patients received alternative androgen-directed therapies while others received palliative radiotherapy and glucocorticoids. The trial schema for VISION is as follows: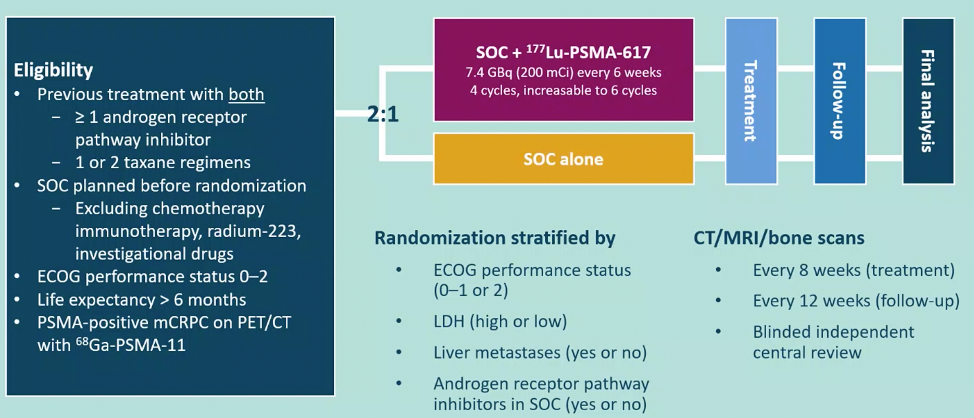
The trial assessed two alternate primary endpoints: radiographic progression-free survival (rPFS) using PCWG3 criteria by independent central review (ICR) and overall survival (OS).
In addition to these two primary endpoints, they also assessed key secondary endpoints of objective response rate (ORR; RECIST v1.1), disease control rate (DCR), and time to first symptomatic skeletal event (SSE) as well as other secondary endpoints including safety and tolerability, biomarkers including PSA, and health-related quality of life and pain.
Among 1,179 screened patients, the VISION trial enrolled 831 patients between June 4, 2018, and October 23, 2019, including 551 patients were allocated to 177Lu-PSMA-617 + SOC and 280 were allocated to SOC only.
As expected in the randomization design, demographic characteristics and baseline features were well balanced between the two treatment groups. Further, pre-randomization treatment was well balanced. In both the rPFS analysis set and among all randomized patients, between 45-50% of patients had received more than one androgen receptor pathway inhibitor and 41-48% of patients had received more than one taxane regime.
Over a median study follow-up of 20.9 month, treatment with 177Lu-PSMA-617+ SOC significantly improved overall survival by a median of 4.0 months (median OS, 15.3 vs 11.3 months; HR, 0.62 [95% CI: 0.52, 0.74]; p < 0.001, one-sided), compared to SOC alone, in the overall cohort of all randomized patients (n=831). The second alternate primary endpoint showed that treatment with 177Lu-PSMA-617 + SOC significantly improved rPFS by a median 5.3 months (median rPFS, 8.7 vs 3.4 months; HR, 0.40 [99.2% CI: 0.29, 0.57]; p < 0.001, one-sided).
While a higher rate of high-grade (grade 3-5) treatment-emergent adverse events was observed with 177Lu-PSMA-617 (28.4% vs 3.9%), overall therapy was well tolerated. In terms of specific adverse events, treatment with 177Lu-PSMA-617+ SOC was associated with increased rates of bone marrow suppression, xerostomia, and nausea and vomiting.
Dr. De Bono concluded his presentation of the VISION trial with the following take-home messages:
- Adding 177Lu-PSMA-617to safely combinable SOC in patients with mCRPC after androgen receptor pathway inhibition and chemotherapy extended overall survival and delayed radiographic disease progression
- 177Lu-PSMA-617was well tolerated
- These findings support the adoption of 177Lu-PSMA-617 as a new treatment option in patients with mCRPC
Presented By: Johann De Bono, MD, MSc, Ph.D., FRCP, FMedSci, Institute of Cancer Research, Royal Marsden Hospital, London, UK
Written By: Zachary Klaassen, MD, MSc – Urologic Oncologist, Assistant Professor of Urology, Georgia Cancer Center, Augusta University/Medical College of Georgia, @zklaassen_md on Twitter during the 2021 European Association of Urology, EAU 2021- Virtual Meeting, July 8-12, 2021.


