(UroToday.com) At the 2022 American Society of Clinical Oncology Annual Meeting held in Chicago and virtually, the oral abstract session focused on Prostate, Testicular, and Penile cancers on Sunday morning included a presentation from Dr. Nitin Vaishampayan discussing subgroup analyses of the VISION trial examining 177Lu-PSMA-617 in men with heavily pre-treated metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC).
Theranostic treatment using 177Lu-PSMA-617has rapidly gained interest in both research and clinical practice spheres. The principle of theranostic approaches rely on targeted delivery of treatment directly to cancer cells: in the case of 177Lu-PSMA-617, the beta-emitter lutetium is targeted to prostate cancer cells using antibodies to the transmembrane protein PSMA (prostate-specific membrane antigen). The VISION trial (NCT03511664) provided the first phase III randomized controlled evidence to support the use of LuPSMA and led to its recent FDA approval. VISION demonstrated that targeted radioligand therapy with lutetium (177Lu) vipivotide tetraxetan ([177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617; 177Lu-PSMA-617) significantly prolonged radiographic progression-free survival (rPFS) and overall survival (OS) when added to standard of care (SoC) in patients with advanced prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) PET-positive metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. At this year’s ASCO meeting, Dr. Vaishampayan provided results regarding post hoc subgroup analyses assessing potential effect modification due to prior and concomitant cancer-directed treatments.
To briefly summarize, the VISION trial enrolled adult patients who had previously received treatment with at least 1 androgen receptor pathway inhibitor (ARPI) and 1–2 taxane regimens for mCRPC. Further, patients had to have evidence of PSMA-positive disease on 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT. These men were randomized 2:1 to 177Lu-PSMA-617 (7.4 GBq Q6W, up to 6 cycles) + SoC or SoC alone. Protocol-permitted SoC excluded cytotoxic chemotherapy, systemic radioisotopes, immunotherapy, or other investigational drugs.
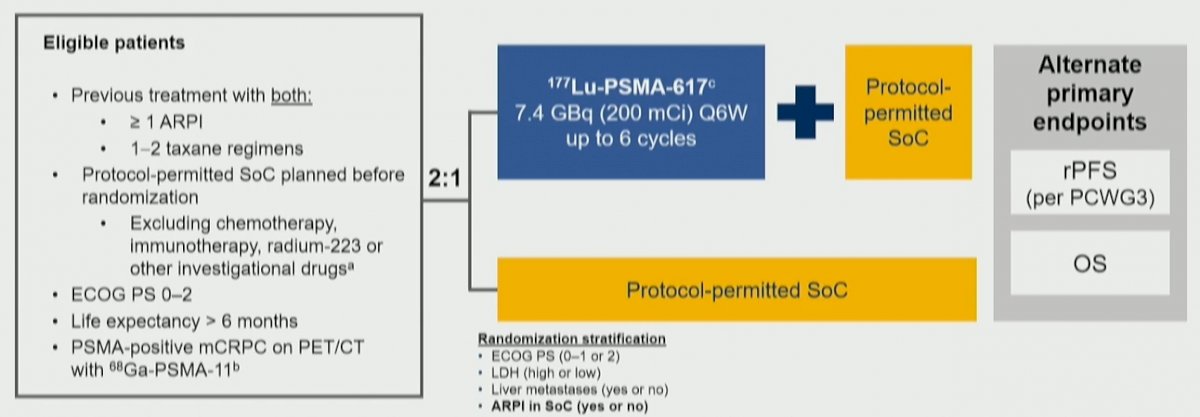
In this analysis, the authors performed exploratory subgroup analyses of rPFS and OS according to prior and concomitant cancer-directed treatments including the number of prior ARPIs; taxane regimens; non-taxane regimens and immunotherapies; prior treatment with bone-sparing agents; 223Ra and PARP inhibitors; and concomitant treatment with ARPIs, radiation therapy, and bone-sparing agents.
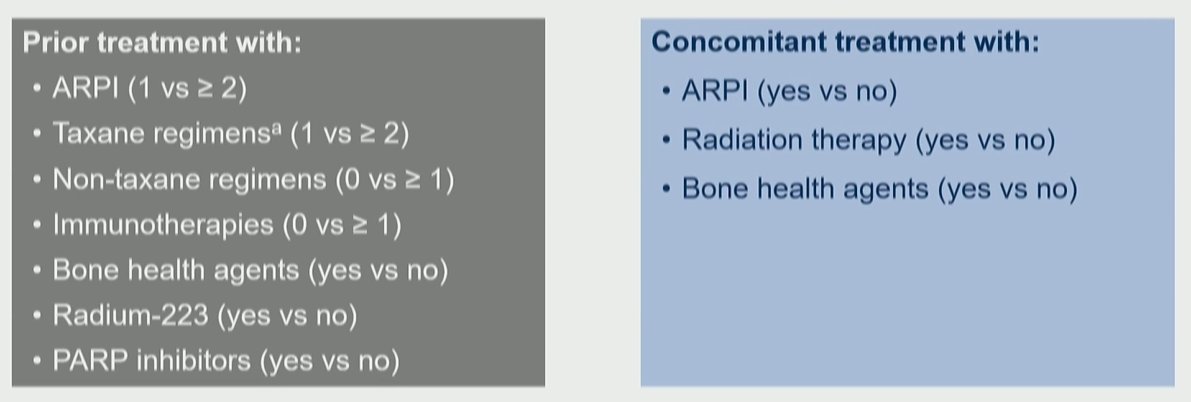
In general, prior and concomitant treatments were generally well balanced between the two study arms. The majority of patients had received one prior line of taxane therapy (65.3%) while the minority had received bone health agents (18.8%), radium-223 (17.4%), and PARP inhibitors (5.5%). Concomitantly, 54.8% of patients received androgen receptor pathway inhibitors and 43.9% received concomitant bone health agents.
The rPFS and OS benefits associated with 177Lu-PSMA-617 in the primary analysis of the VISION trial were consistent across all prior treatment subgroups, including androgen receptor pathway inhibitors, the number of taxane regimes, non-taxane regimes, immunotherapies, bone health agents, radium-223, and PARP inhibitors.
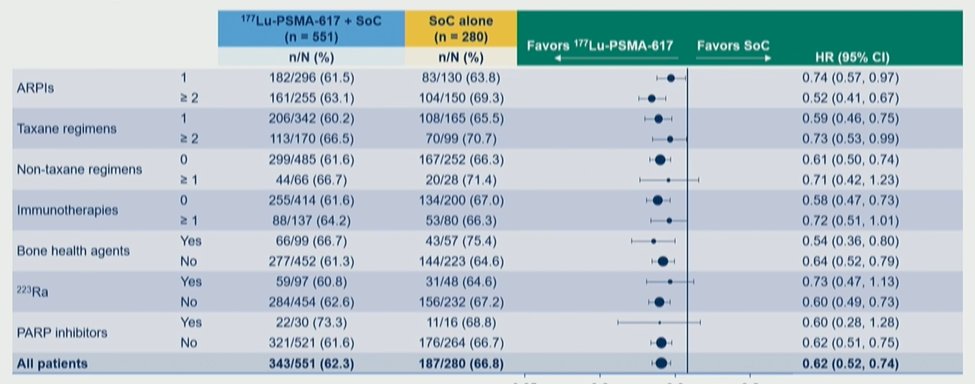
He focused then on results according to the number of prior including androgen receptor pathway inhibitors noting that both rPFS and OS were improved with the use of 177Lu-PSMA-617 in patients with one prior line of therapy or two or more lines of therapy. A similar observation was made according to the number of lines of prior taxane therapies with consistent benefits seen for the use of 177Lu-PSMA-617. Notably, there were benefits in patients who had not received a second prior taxane.
There were also consistent benefits regardless of concomitant systemic and radiation therapy as part of SoC. While Dr. Vaishampayan first presented data on rPFS, most notably, there was a consistent benefit in overall survival whether patients received concomitant androgen receptor pathway inhibitors, bone health agents, or radiotherapy.
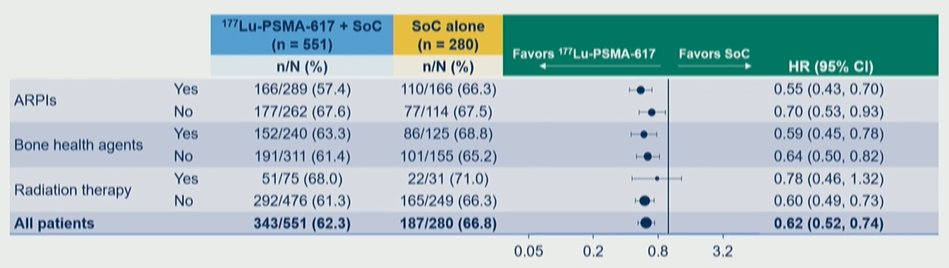
Thus, the authors conclude that the clinical efficacy of 177Lu-PSMA-617 was observed to be consistent regardless of prior treatment or SoC chosen, suggesting that disease biology rather than prior and concomitant treatment context drives outcomes. There is a particular signal for prolonged overall survival in patients who received one line of prior taxane therapy and in those receiving concurrent androgen receptor pathway inhibitors.
Presented by: Nitin Vaishampayan, MD, BA, Assistant Professor of Clinical Radiation Oncology, Wayne State University


