(UroToday.com) The 2023 Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) Annual Meeting held in Chicago, IL between June 24th and 27th, 2023 was host to a session on urologic malignancies. Following his earlier presentation of the ZIRCON phase 3 study results in the overall cohort, Dr. Calais next presented results from the UCLA cohort of this trial.
The carbonic anhydrase IX (CAIX) transmembrane protein was initially described in 1986, with the identification of anti-CAIX murine monoclonal antibodies. Girentuximab, an anti-CAIX antibody, was first engineered in 1998 and subsequently licensed to Wilex AG (now HDPharma). In 2009, the phase 3 REDECT trial was completed and subsequently published in 2013.1 This study utilized iodine-124-girentuximab PET/CT for the characterization of renal masses in patients planned for surgical resection. In 2017, girentuximab was licensed to Telix, and subsequently the confirmatory phase III ZIRCON trial of TLX250-CDx was commenced (completed in 2022).
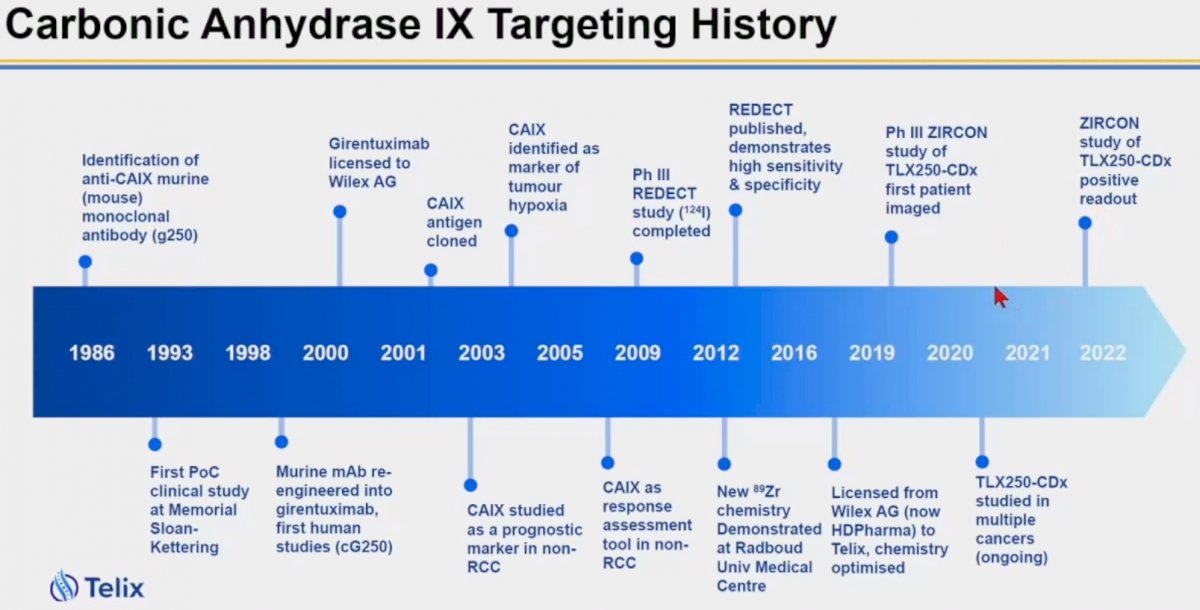
The REDECT trial was an open-label multicenter study of iodine-124-girentuximab PET/CT in patients with renal masses who were scheduled for surgical resection. PET/CT and contrast-enhanced CT of the abdomen were performed two to six days after intravenous (124)I-girentuximab administration and before resection of the renal mass(es). Among the 195 patients included, this test demonstrated an average sensitivity and specificity of 86%, versus 76% and 57%, respectively, for contrast-enhanced CT.1 In September 2012, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) mandated an outcome-based trial or a diagnostic performance confirmatory trial, prior to potential approval. This led to the opening of the confirmatory REDECT 2 trial. Concurrently, Wilex opened the ARISER trial, which was a randomized phase 3 trial of 864 patients with resected, high-risk clear cell RCC randomized to either adjuvant girentuximab (RENCAREX®) or placebo. 
This trial failed to demonstrate a clinical benefit for girentuximab in this setting,2 and Wilex subsequently went out of business in 2013, with the REDECT 2 trial prematurely closed. In 2017, Telix acquired the licensing for cG250 and initiated the diagnostic performance confirmatory trial, ZIRCON.
ZIRCON is an international, multicenter trial conducted at 36 sites across nine countries between 2019 and 2022. This trial included patients with a single, indeterminate cT1 renal mass (i.e., ≤7 cm) suspicious for clear cell RCC, detected on CT or MRI. All patients were scheduled for surgical removal (histologic reference standard). Patients received 89Zr-girentuximab on day 0. They subsequently underwent abdominal PET/CT imaging five days (+/- 2) following tracer administration. PET/CT imaging findings were evaluated using blinded central imaging review. All patients were subsequently planned for partial or radical nephrectomy, with central histology review of surgical specimens, within 90 days of tracer administration.
This study met its co-primary endpoints of sensitivity and specificity in the cT1 cohort, with sensitivity and specificity ≥84% in all three independent readers (86% and 87% overall). This exceeded the confirmatory trial sensitivity and specificity targets of 70% for each. This study also met its key secondary endpoints, namely sensitivity and specificity targets in the cT1a renal mass(4 cm or less) subgroup.
Of the 300 patients, 33 (11%) were enrolled at UCLA. All tumors were staged as cT1, with tumor size ranging between 1.5 and 6.7 cm, as per the inclusion criteria. Of the 33 masses, 22 (67%) were clear cell RCC. Local read results by Dr. Calais demonstrated that the PET was positive in 19/22 clear cell RCC patients (i.e., sensitivity of 87%). All 11 benign and non-clear cell RCC masses were PET negative (i.e., specificity of 100%). The median SUV max was significantly higher in the clear cell RCC masses (28 versus 5). Of the 12 tumors with chromosomal 3p loss, 11 were PET positive. All 10 tumors with positive CAIX by immunohistochemistry were detected on PET/CT.
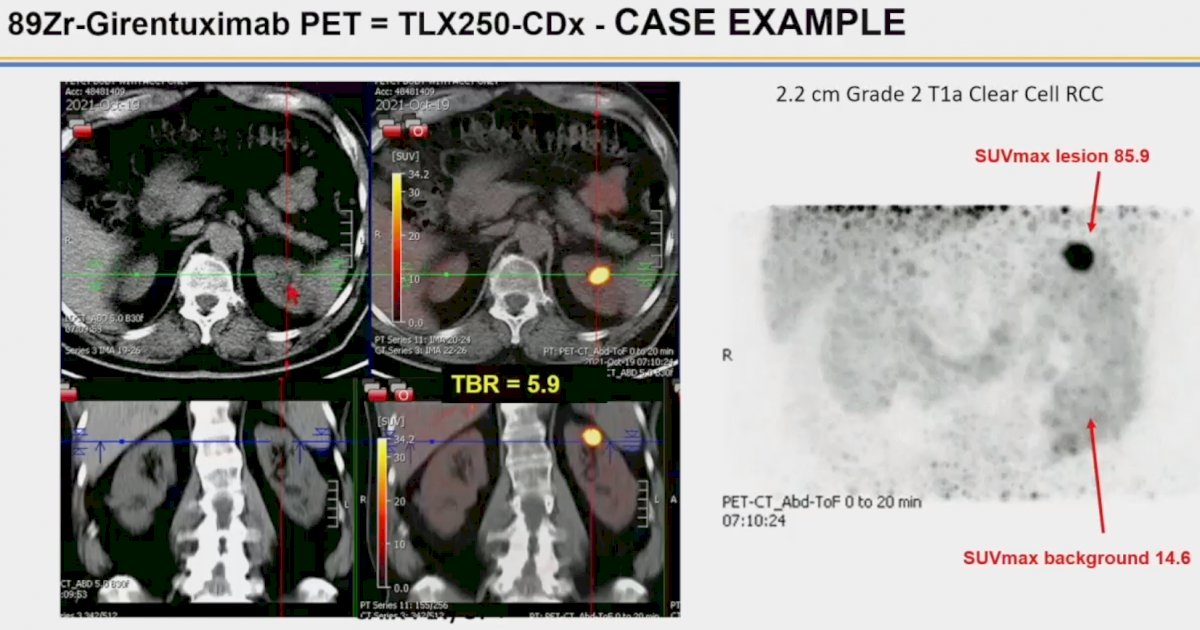
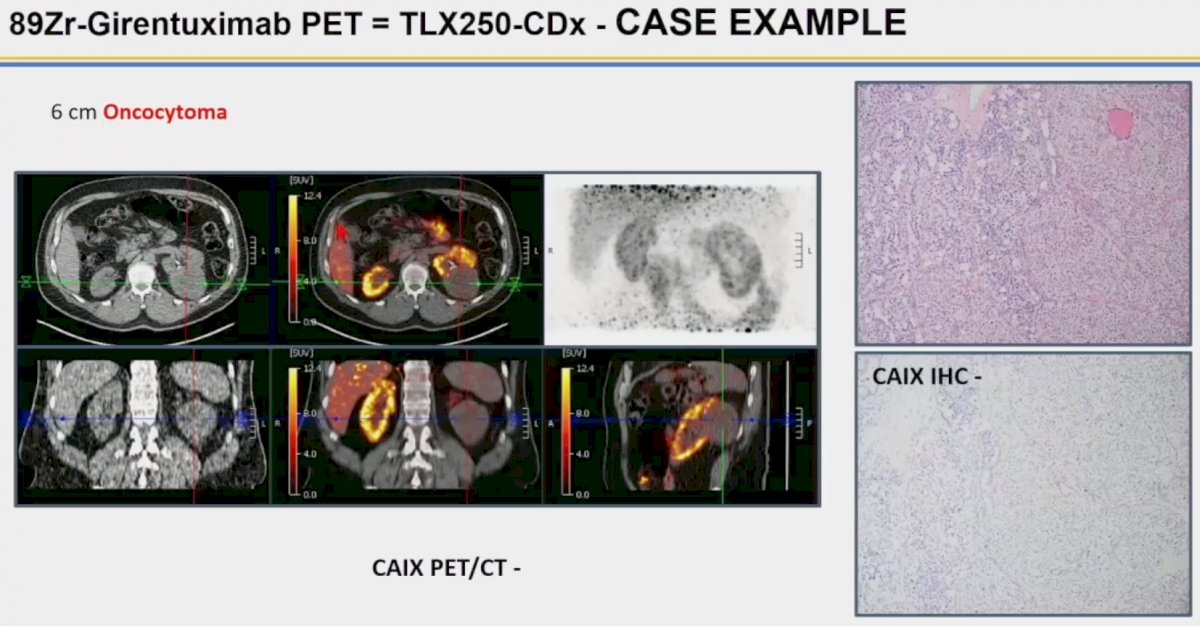
The image below demonstrates the case of a 6 cm oncocytoma. As noted below, we see a large photopenic area in the left kidney with no tracer uptake, corresponding to the oncocytic neoplasm.
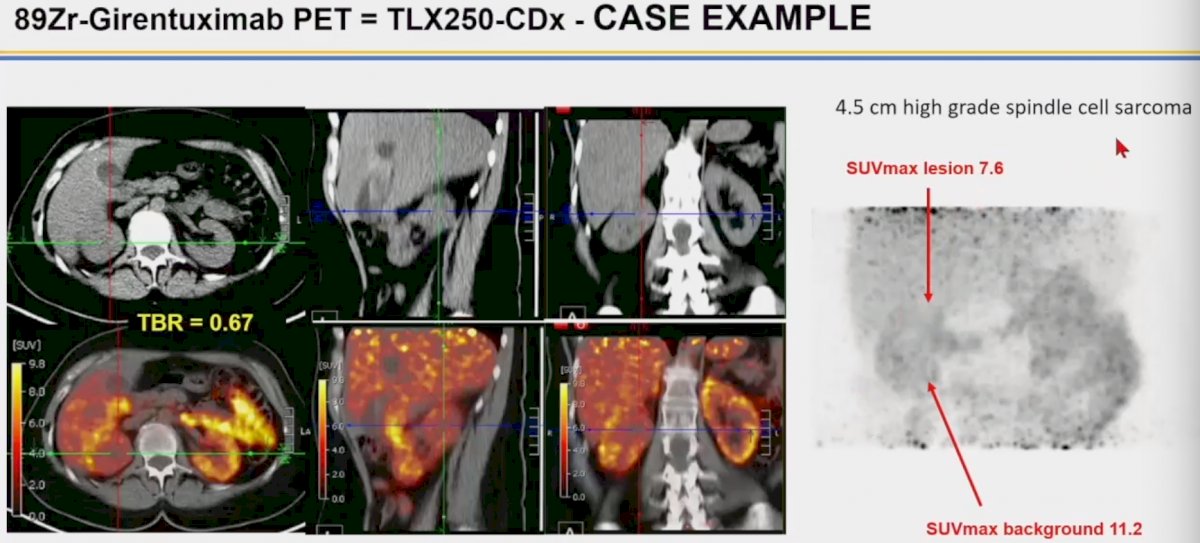
Dr. Calais highlighted a case of a patient with a 4.5 cm high-grade spindle cell sarcoma. This lesion was tracer negative as demonstrated below. The key takeaway from this example is the CAIX is not expressed by all malignancies, and a negative 89Zr-girentuximab PET does not rule out the presence of underlying malignancy.
Results from the UCLA subset compared favorably to those from the ZIRCON full cohort and the REDECT trial, as summarized in the table below.

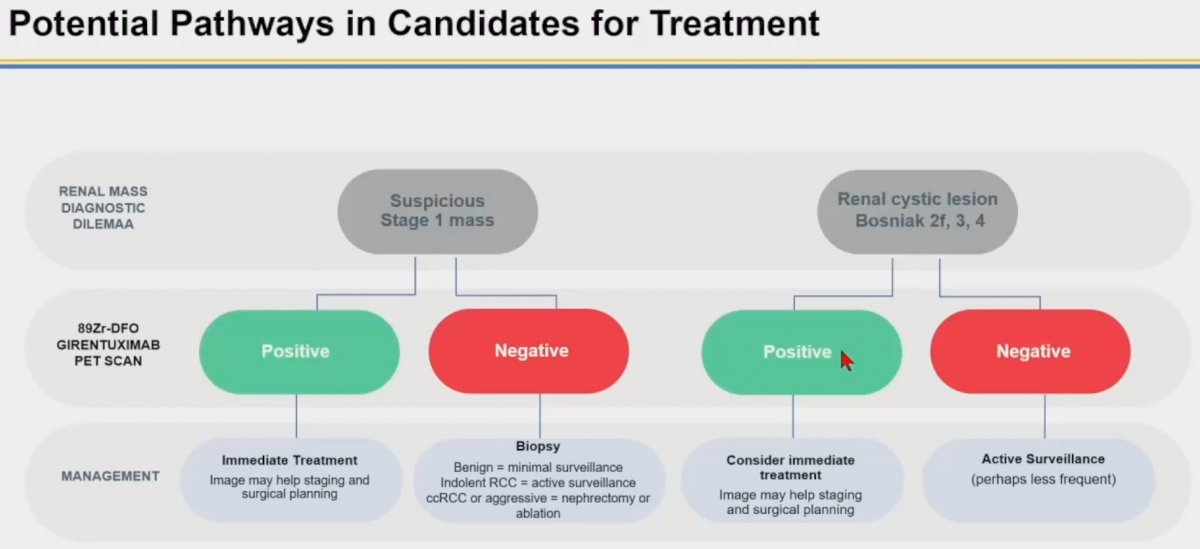
How can we leverage the results of the ZIRCON trial to inform our clinical practice? Dr. Calais suggested the following potential pathways in treatment candidates with either cT1 masses or complex renal cysts (Bosniak 2F, 3, or 4). The greatest utility of this scan appears to be in patients with positive PSMA PET results. Given the high positive predictive value of this scan (93% and 100% in the overall and UCLA cohorts), patients with positive findings may proceed directly to surgery, per Dr. Calais. Conversely, patients with negative findings would likely benefit from a biopsy to discern benign masses from those of non-clear cell RCC malignant etiology.
Presented by: Jeremie Calais, MD, MSc, Associate Professor of Nuclear Medicine and Theranostics, Department of Molecular and Medical Pharmacology, University of California, Los Angeles, CA
Written by: Rashid K. Sayyid, MD, MSc – Society of Urologic Oncology (SUO) Clinical Fellow at The University of Toronto, @rksayyid on Twitter during the 2023 Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) Annual Meeting, Chicago, IL, Sat, June 24 – Tues, June 27, 2023.
References:- Divgi CR, et al . Positron emission tomography/computed tomography identification of clear cell renal cell carcinoma: results from the REDECT trial. J Clin Oncol, 2013;31(2):187-94.
- Chamie K, et al. Adjuvant Weekly Girentuximab Following Nephrectomy for High-Risk Renal Cell Carcinoma: The ARISER Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol, 2017;3(7):913-20.


