(UroToday.com) The 2024 ASTRO annual meeting included a session on prostate cancer, featuring a presentation by Yuan-Hong Lin discussing the impact of hyaluronic acid rectal spacer quality score and Fisher-Valuck spacer symmetry score on rectal dosimetry and acute and late gastrointestinal toxicity outcomes. Moderately hypofractionated radiotherapy to the prostate is now the standard of care for management of localized prostate cancer. However, a prior meta-analysis demonstrated a 9.1% greater absolute risk of >= grade 2 acute gastrointestinal toxicity compared to conventionally fractionated radiotherapy.1
Rectal spacers, either in the form of hyaluronic acid or hydrogel, have been shown to reduce rectal dosimetry, as well as acute and late gastrointestinal toxicity for patients undergoing prostate radiotherapy. Quality of the rectal spacer implant has been shown to impact the rectal dosimetry and gastrointestinal toxicity outcomes, and metrics such as Spacer Quality Score2 and Fischer-Valuck score3 have been developed to explore rectal spacer implant quality. Thus, the objective of this study was to assess implant quality using the modified Spacer Symmetry Score and Fisher-Valuck scores achieved in men with localized prostate cancer treated with moderately hypofractionated external beam radiotherapy who underwent stabilized hyaluronic acid rectal spacer implant, and its impact on acute and late gastrointestinal toxicity.
This retrospective multi-institutional review involved 100 consecutive men with localized prostate cancer treated with moderately hypofractionated external beam radiotherapy (60 Gy or 62 Gy in 20 fractions) and underwent hyaluronic acid rectal spacer insertion, treated between June 2020 and September 2022. Statistical metrics were used to assess patient and disease characteristics, and acute and late gastrointestinal toxicity were assessed using CTCAE v5. Implant quality was assessed using the modified Spacer Symmetry Score (recto-prostatic separation), Fisher-Valuck score (symmetry), and spacer rectal wall infiltration evaluated on post-implant T2-weighted MRI axial slices. Rectal wall infiltration was independently assessed by an MRI prostate specialist radiologist. Spacer Quality Score, rectal wall infiltration, and Fisher-Valuck scoring were performed according to prior publications:2-3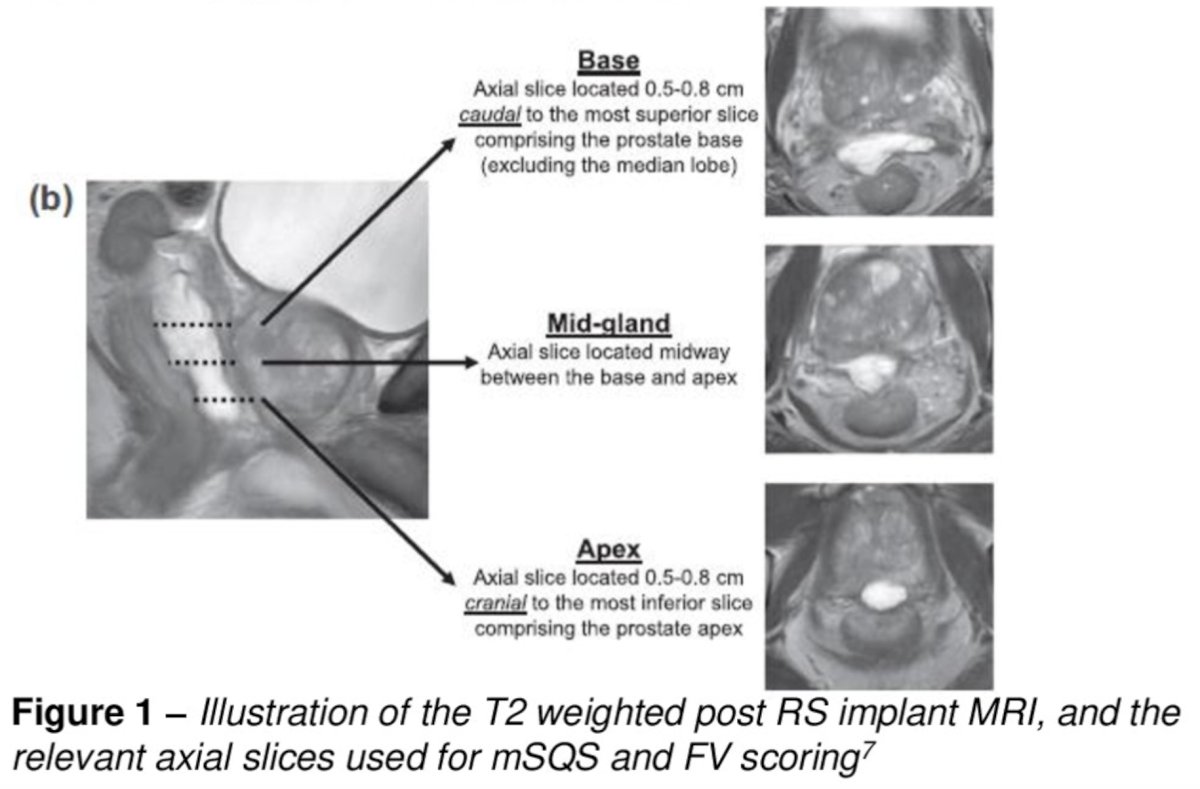
The modified Spacer Symmetry Score scores were used to stringently account for PTV expansions:
- Score 2: >=10 mm recto-prostatic separation
- Score 1: 6-9 mm recto-prostatic separation
- Score 0: <=5 mm recto-prostatic separation
The mean age was 74.6 years (SD 6.0 years), 54 patients had unfavourable intermediate-risk prostate cancer, 33 had favorable intermediate-risk prostate cancer and 9 had low-risk prostate cancer. There were 88 patients treated to 60 Gy/20#, while 12 patients were treated to 62 Gy/20#. Among the 100 rectal spacer implants, 98% were deemed “very easy” by the injector and 2% were deemed “easy”. Overall, a modified Spacer Symmetry Score of 1 (“good”) was achieved in 74 patients, score of 2 ("excellent") in 24 patients, and a score of 0 occurred in just 2 patients. Moreover, 97% of the injectors successfully shaped hyaluronic acid to achieve symmetrical rectal spacing with Fisher-Valuck score of 1: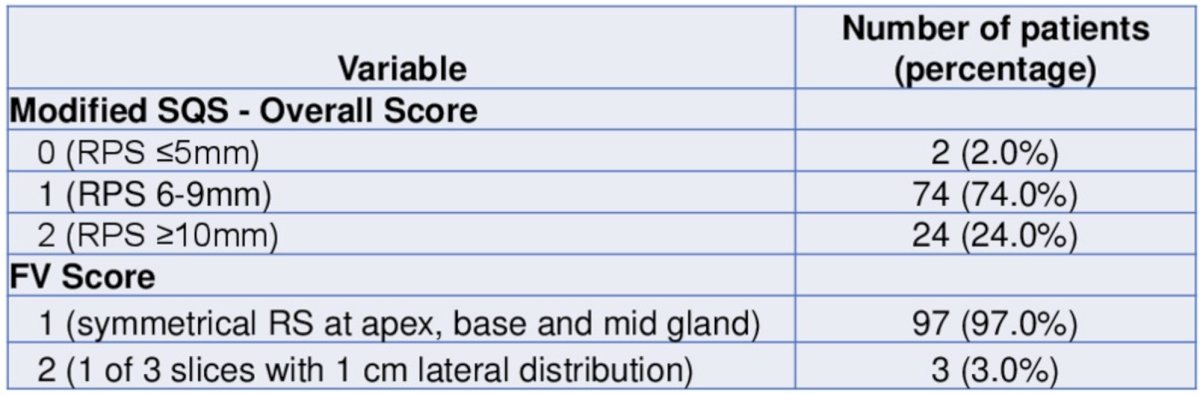
The median rectal V36 was 13.2% (IQR 9.2-17.5), V42 was 8.4% (IQR 5.4-12.3), V48 was 5.1% (IQR 2.7-8.2), V54 was 2.1% (IQR 0.9-4.5), and V57 was 0.9% (IQR 0.2-2.3):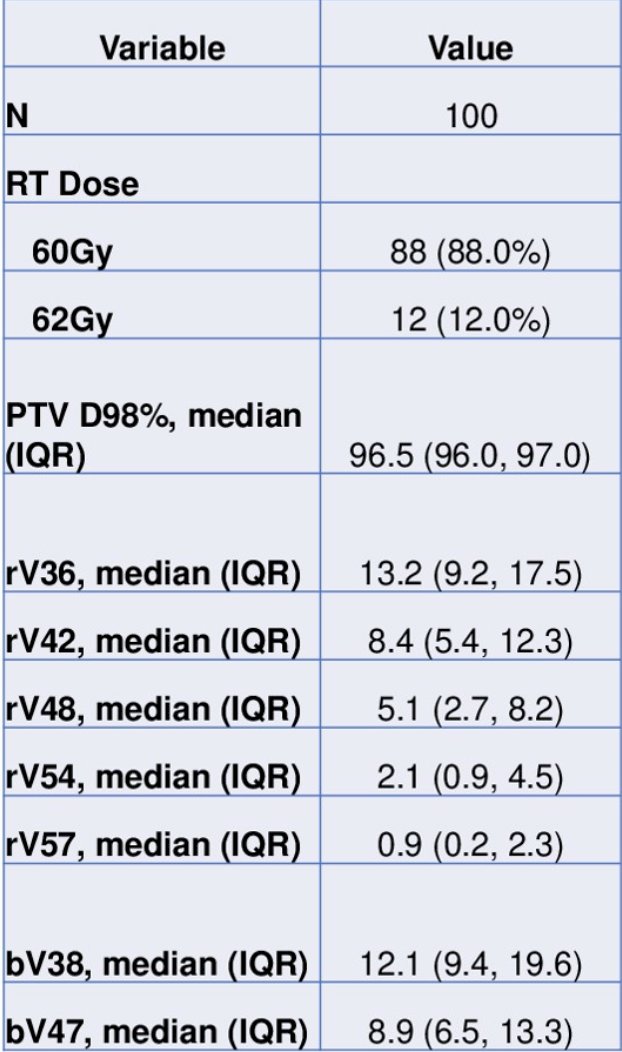
Seven acute grade 1 and five late grade 1 gastrointestinal toxicities were recorded. There was no grade 2+ acute or late gastrointestinal toxicity. No statistically significant association was identified between Fisher-Valuck and Spacer Quality Score with acute or late gastrointestinal toxicity incidence. Only 1 patient experienced implant rectal wall infiltration and the rectal wall infiltration was reversed with hyaluronidase, with no significant sequelae reported. This patient was subsequently reimplanted successfully with hyaluronic acid rectal spacer and completed external beam radiotherapy uneventfully. The median follow-up was 1.68 years (IQR 1.28-2.23), with only one regional recurrence reported.
Dr. Lin concluded his presentation discussing the impact of hyaluronic acid rectal spacer quality score and Fisher-Valuck spacer symmetry score on rectal dosimetry and acute and late gastrointestinal toxicity outcomes with the following take-home points:
- The majority (97%) of patients who underwent hyaluronic acid rectal spacer implant had easily achieved high-quality rectal spacer (both modified Spacer Quality Scores 1-2 and Fisher-Valuck score 1)
- This translated to low rectal doses and low incidence of acute and late grade 1 gastrointestinal toxicities
- Stabilized hyaluronic acid rectal spacer may be considered in patients undergoing hypofractionated external beam radiotherapy to the prostate.
Presented by: Yuan-Hong Lin, MD, Rheumatologist, Alfred Health, Macleod, Victoria, Australia
Written by: Zachary Klaassen, MD, MSc – Urologic Oncologist, Associate Professor of Urology, Georgia Cancer Center, Wellstar MCG Health, @zklaassen_md on Twitter during the 2024 American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, Sun, Sept 29 – Wed, Oct 2, 2024.
References:
- Datta NR, Stutz E, Rogers S, et al. Conventional versus hypofractionated radiation therapy for localized or locally advanced prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis along with therapeutic implications. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2017;99(3):573-589.
- Grossman CE, Folkert MR, Lobaugh S, et al. Quality metric to assess adequacy of Hydrogel Rectal Spacer placement for prostate radiation therapy and association of metric score with rectal toxicity outcomes. Adv Radiat Oncol. 2023 Jan 24;8(4):101070.
- Fischer-Valuck BW, Chundury A, Gay H, et al. Hydrogen spacer distribution within the perirectal space in patients undergoing radiotherapy for prostate cancer: Impact of spacer symmetry on rectal dose reduction and the clinical consequences of hydrogel infiltration into the rectal wall. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2017 May-Jun;7(3):195-202.


