(UroToday.com) The 2023 American Urological Association (AUA) annual meeting held in Chicago, IL between April 28 and May 1st, 2023, was host to the Arab Association of Urology sectional session. Dr. Waleed Hassen discussed the current state of prostate cancer in the Middle East.
Dr. Hassen began his presentation by highlighting that while the incidence of prostate cancer may appear low in the Middle East, this is likely secondary to low screening rates and poor public awareness. This is illustrated in the two figures below. The first figure illustrates that the 2020 age-standardized incidence rates of prostate cancer in the Middle Eastern countries are consistently low (light blue shading: <14.5 to 14.5-32.3 diagnoses per 100,000).

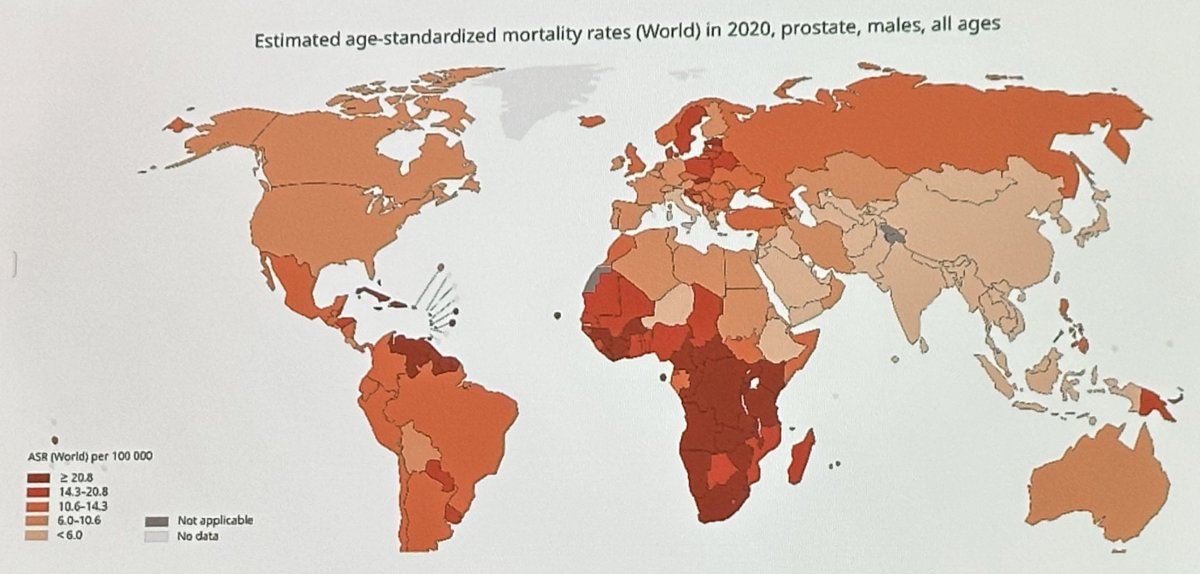
Conversely, it appears that the 2020 age-standardized mortality rates for these countries are disparately higher as demonstrated by the darker orange shading (6.0-10.6 mortalities per 100,000) in the figure below.
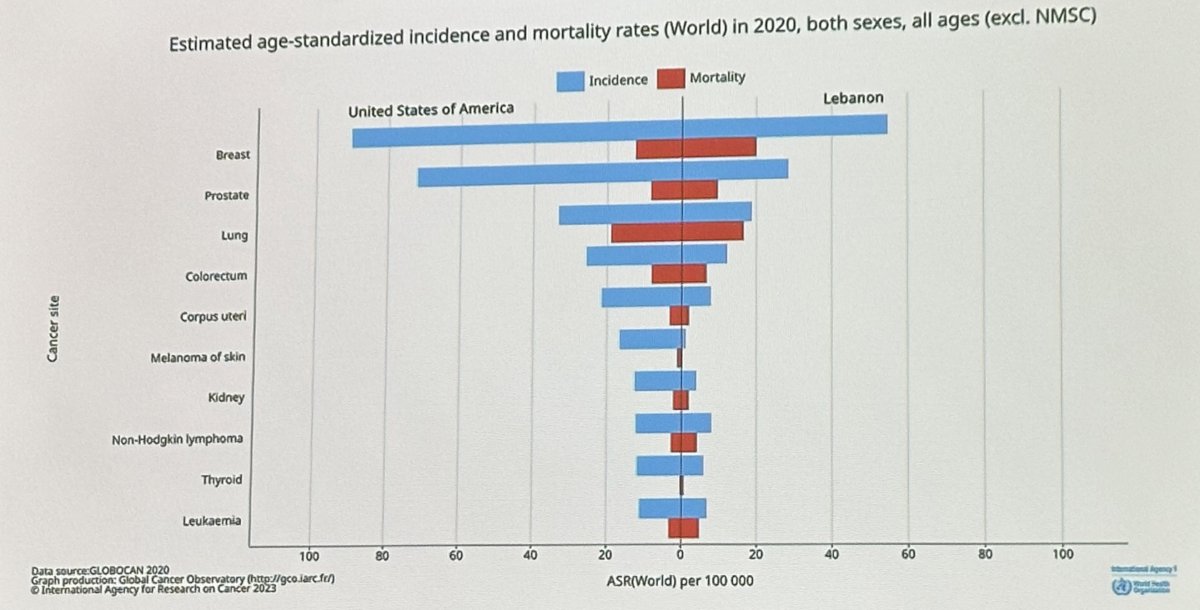
This issue is further highlighted by a Lebanese study of various malignancies that demonstrates equivalent age-standardized prostate cancer mortality rates for Lebanese men, compared to US men, although the corresponding incidence of prostate cancer in US men was almost three-fold higher, again strongly suggestive of poor screening patterns in this region.
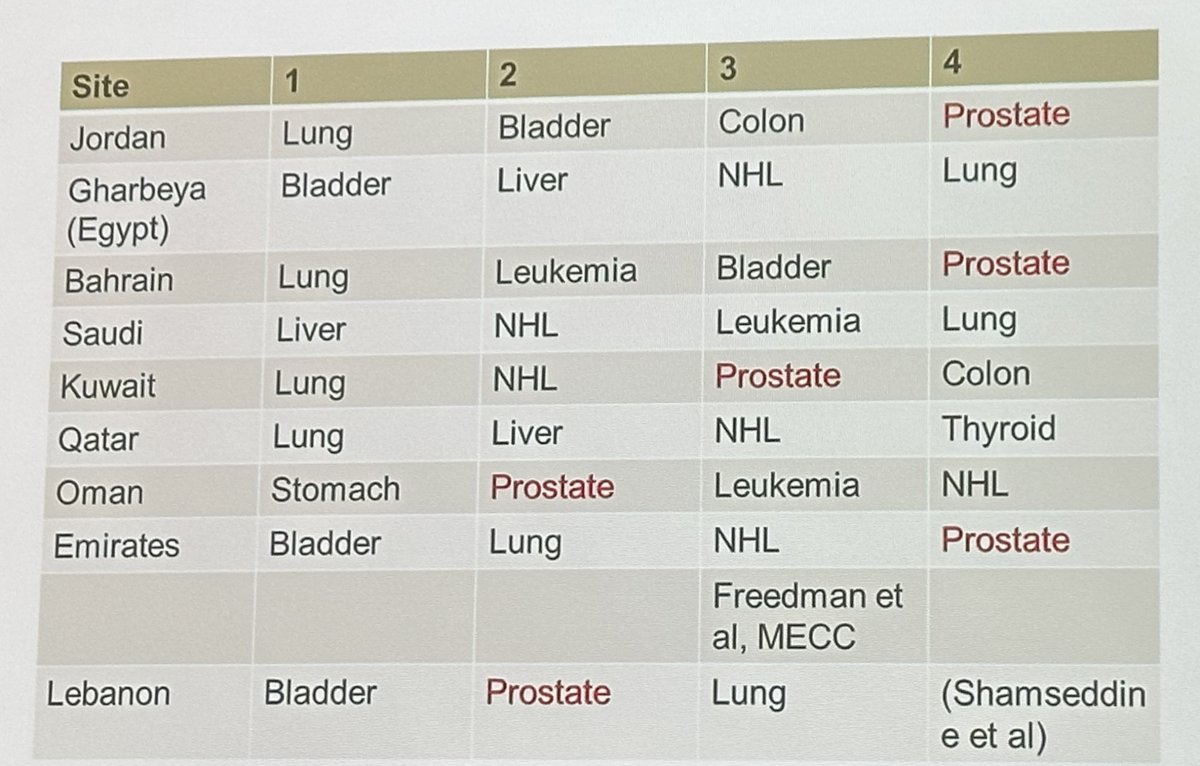
The scope of this problem remains poorly understood. Small regional registries from the Middle East show significant variations in the rank order of various malignancies, which may be emblematic of underlying screening patterns, as well as potential genetic and environmental factors.
But are incidence rates truly less in this region or is this simply a result of screening/referral patterns? Presented in abstract format at AUA 2017, Hassan et al included a total of 330 screened Arab patients who were referred to Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi over a 24-month period. The median age of the cohort was 63 years, of whom 22% were Emirati nationals and 78% from other Middle Eastern countries. Median PSA o the cohort was 8.9 ng/ml (range: 3.4 – 784 ng/ml). Among these 330 patients, the cancer detection rate was 42%:
- Grade Group 2-3: 50%
- Grade Group 4 or worse: 24%
- 17% had metastases at diagnosis
Given these clear disparities in prostate cancer screening/incidence and mortality rates, modifications to the NCCN guidelines on Prostate Cancer have been proposed and implemented for men in the Middle East and North African region. These guidelines, and others, have highlighted key issues with prostate cancer care in the Middle Eastern region:
- Lack of screening
- Most patients present with advanced disease
- Up to 60% of RP specimens have evidence of pT3 or worse disease
- Poor access to primary care
- Reactive, as opposed to a proactive, health system
- Wide variability in resources, with significant clustering of resources in certain cities
- Morbidity (e.g., potency and continence) secondary to treatment is unacceptable to many patients
- Poor surgical training in many Middle Eastern centers
- Surgical volume and experience have consistently been shown to be associated with improved oncologic and perioperative outcomes1-4
- Few high-volume centers in the region with surgical training volume lacking
- Among polled Middle Eastern urologists, 40% reported performing <10 RPs in training
Furthermore, there is a clear shortage of surgical equipment in the region, with <1% of robotic Da Vinci systems in the Arab region. This limitation also extends to the number of radiotherapy machines per capita with 1 – 5 machines per a million people in this region. This issue will only be further exacerbated by the fact that the population of North Africa and The Middle East is estimated to grow from ~450 million currently to 750 by 2050. As such, further resources in this region are clearly needed to “keep up” with the growing population.

Dr. Hassen concluded his presentation with the following take home messages:
- While the incidence of prostate cancer appears to be less than that of Western countries, this is likely secondary to awareness/screening patterns as opposed to a truly lower incidence
- Prostate cancer is a significant source of cancer-related morbidity in this region
- Numerous obstacles are currently present to deliver what would be deemed “standard of care” to the region
Presented by: Waleed A. Hassen, MD, Department Chair, Urology, Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi, Abu Dhabi, UAE
Written by: Rashid K. Sayyid, MD, MSc – Society of Urologic Oncology (SUO) Clinical Fellow at The University of Toronto, @rksayyid on Twitter during the 2023 American Urological Association (AUA) Annual Meeting, Chicago, IL, April 27 – May 1, 2023
References:
- Hu JC, Gold KF, Pashos CL, et al. Role of surgeon volume in radical prostatectomy outcomes. J Clin Oncol 2003;21(3):401-405.
- Klein EA, Bianco FJ, Serio AM, et al. Surgeon Experience is Strongly Associated with Biochemical Recurrence after Radical Prostatectomy for all Preoperative Risk Categories. J Urol 2008;179(6):2212-2216.
- Alemozaffar M, Duclos A, Hevelone ND, et al. Technical Refinement and Learning Curve for Attenuating Neurapraxia During Robotic-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy to Improve Sexual Function. Eur Urol 2012;61(6):1222-12228.
- Ju IE, Trieu D, Chang SB, et al. Surgeon Experience and Erectile Function After Radical Prostatectomy: A Systematic Review. Sex Med Rev 2021;9(4):650-658.








