(UroToday.com The 2024 ASTRO annual meeting included a session on prostate cancer, featuring a presentation by Dr. Anne Hong discussing rectal wall infiltration with a hyaluronic acid-based rectal spacer reversal protocol. Radiation therapy is a mainstay of treatment for prostate cancer, however, treatment may cause gastrointestinal toxicity given that the rectum is an organ at risk. Stabilized hyaluronic acid has recently been approved for use as a rectal spacer and reduces gastrointestinal toxicity in this setting.1
It has several advantages, including its reversibility using hyaluronidase, which is particularly beneficial in cases of rectal wall infiltration. The use of non-reversible rectal spacers may lead to severe adverse outcomes such as mucosal ulceration, pelvic abscess, and recto-prostatic fistula after rectal wall infiltration. As such, Dr. Hong and colleagues assessed the outcomes of inadvertent rectal wall infiltration by stabilized hyaluronic acid rectal spacers, specifically assessing the feasibility of reversal and gastrointestinal toxicity.
This was a retrospective analysis of patients who had inadvertent rectal wall infiltration following the use of stabilized hyaluronic acid rectal spacers conducted in five institutions in Australia (2021-2024). More than 5,000 patients have had stabilized hyaluronic acid rectal spacing with the majority undergoing MRI simulation. Patients with rectal wall infiltration were identified based on post-procedural MRI. Data collection included patient demographics, delays in radiation therapy, grade of the rectal wall infiltration and symptoms, and management of the rectal wall infiltration. The patients were followed up during and post radiation therapy and assessed for rectal complications. The reversal procedure has previously been described.2
A total of 16 prostate cancer patients were identified to have rectal wall infiltration after stabilized hyaluronic acid spacer insertion: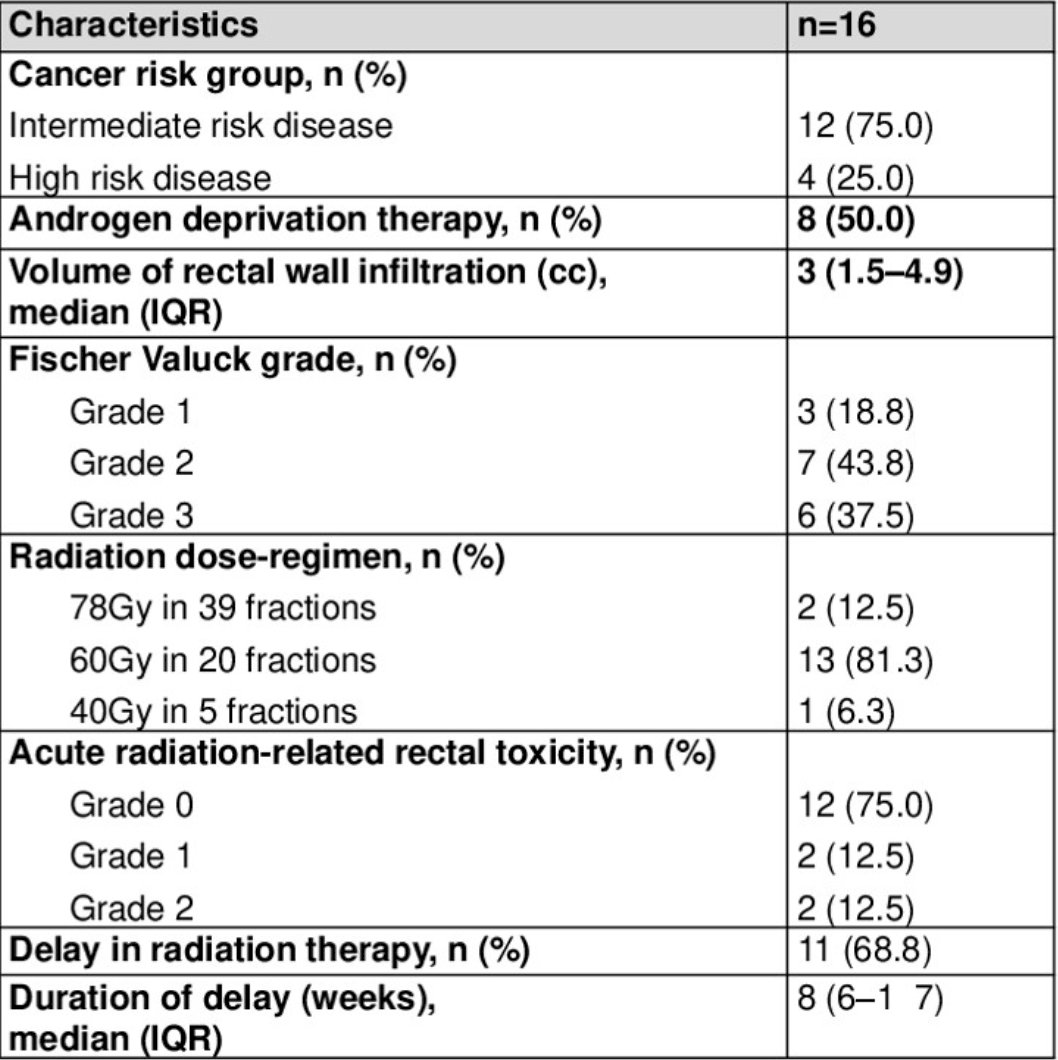
The grade of rectal wall infiltration as defined by Fischer Valuck criteria were as follows:3
- Grade 1, n = 5
- Grade 2, n = 6
- Grade 3, n = 5

The median volume of misplaced stabilized hyaluronic acid was 2.8 cc from an average total of 9 cc used. No post-procedural gastrointestinal symptoms were reported, and digital rectal examination did not detect abnormalities in any patients. A sigmoidoscopy was performed in 12 patients including all 5 with grade 3 rectal wall infiltration, and all of these showed intact rectal mucosa: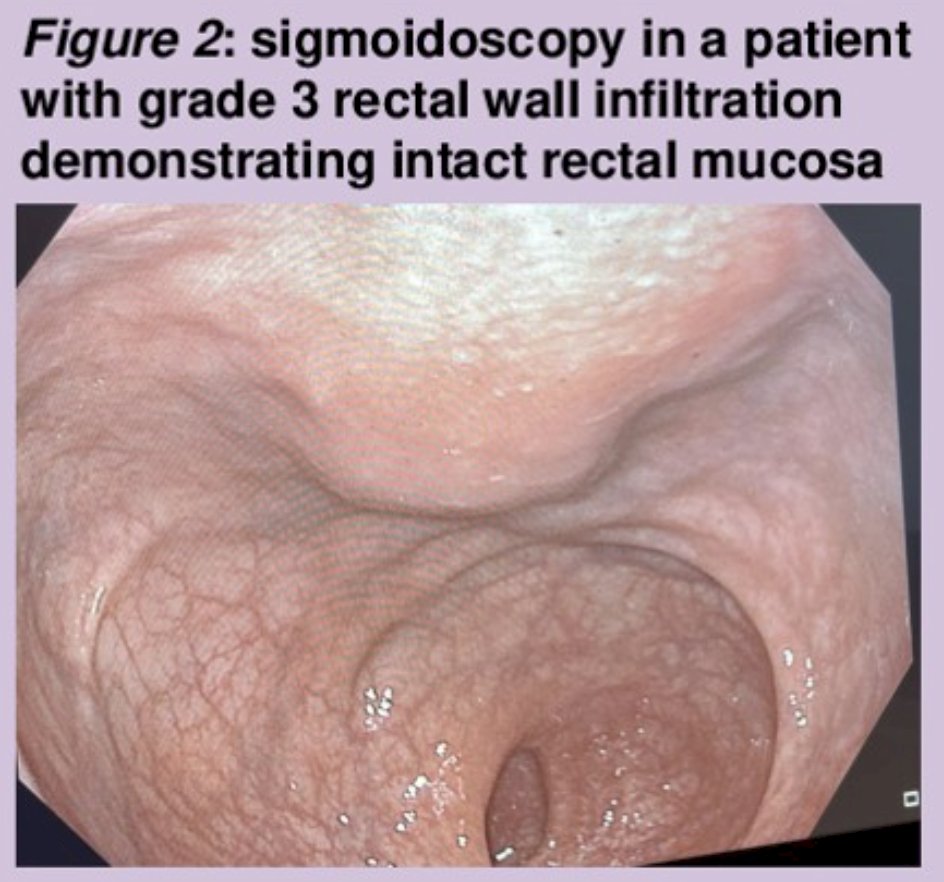
Seven patients underwent targeted reversal procedures while 9 patients were monitored. The Fischer Valuck grading and reversal did not demonstrate an association (Chi-squared test, p = 0.41). Of those who underwent reversal procedures, the median volume of misplaced hyaluronic acid is 4 mL (mean 3.8 mL), compared to 1.5 mL (mean 2.1 mL) in those who did not undergo reversal (Mann-Whitney U test, p = 0.10). All 7 patients who underwent reversal with hyaluronidase were successful, and no post-reversal complications were reported.
One patient underwent successful reinsertion of stabilized hyaluronic acid following reversal. During the reinsertion procedure, hydro dissection using normal saline was performed before stabilized hyaluronic acid placement to ensure positioning within the perirectal fact. The proceduralist rated the re-insertion as “easy” and a subsequent pelvic MRI confirmed the stabilized hyaluronic acid was correctly placed before initiation of radiotherapy. Initiation of radiation therapy was delayed in 11 cases by a median of 8 weeks. Of the cases where radiation therapy was not delayed, the rectal wall infiltration volume ranged from 0.5 mL to 2 mL. During delayed radiation therapy, ADT was continued and all patients completed their radiotherapy as planned. On follow-up, acute rectal toxicity was experienced by four patients. Using the CTCAE score, two patients experienced grade 1 rectal toxicity, and two patients experienced grade 2 rectal toxicity.
Dr. Hong concluded her presentation discussing rectal wall infiltration with a hyaluronic acid-based rectal spacer reversal protocol with the following take-home points:
- Stabilized hyaluronic acid is increasingly used as a rectal spacer to reduce radiation-related gastrointestinal side effects in prostate cancer treatment
- Rectal wall infiltration is uncommon but a potentially serious complication. However, rectal wall infiltration can be safely managed using either observation or reversal. While surgical removal remains an option, it was not required in this study
- Additional key messages:
- Sigmoidoscopy may not be routinely required if the patient is asymptomatic and digital rectal examination is normal
- The decision to reverse a rectal wall infiltration is dependent on patient symptoms, clinical assessment, and volume of rectal wall infiltration.
- It is possible to reinsert stabilized hyaluronic acid after a reversal procedure.
Presented by: Anne Hong, MD, Urology Research Fellow, Austin Health, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia
Written by: Zachary Klaassen, MD, MSc – Urologic Oncologist, Associate Professor of Urology, Georgia Cancer Center, Wellstar MCG Health, @zklaassen_md on Twitter during the 2024 American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, Sun, Sept 29 – Wed, Oct 2, 2024.
References:
- Mariados NF, Orio 3rd PF, Schiffman Z, et al. Hyaluronic acid spacer for hypofractionated prostate radiation therapy: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2023 Apr 1;9(4):511-518.
- Hong A, Ischia J, Chao M. Case report: Reversal of hyaluronic acid rectal wall infiltration with hyaluronidase. Front Oncol. 2022;12:870388
- Fischer-Valuck BW, Chundury A, Gay H, et al. Hydrogen spacer distribution within the perirectal space in patients undergoing radiotherapy for prostate cancer: Impact of spacer symmetry on rectal dose reduction and the clinical consequences of hydrogel infiltration into the rectal wall. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2017 May-Jun;7(3):195-202.