(UroToday.com) The 2024 South Central AUA annual meeting included a session on kidney cancer, featuring a presentation by Dr. Kelly Bree discussing indications and outcomes for ablation therapy in renal masses. Dr. Bree notes that each of the AUA, EAU, and NCCN make statements in their guidelines regarding ablation of renal masses. The following is supported by the AUA:
- Statement 25: Clinicians should consider thermal ablation as an alternate approach for the management of cT1a solid renal masses <3 cm in size. For patients who elect thermal ablation, a percutaneous technique is preferred over a surgical approach whenever feasible to minimize morbidity. (Moderate Recommendation; Evidence Level: Grade C)
- Statement 26: Both radiofrequency ablation and cryoablation may be offered as options for patients who elect thermal ablation. (Conditional Recommendation; Evidence Level: Grade C)
The following is supported by the EAU:
- Offer active surveillance or tumor ablation to frail and/or comorbid patients with small renal masses (Strength rating: Weak)
- Perform a percutaneous renal mass biopsy prior to, and not concomitantly with, thermal ablation (Strength rating: Strong)
- When thermal ablation or active surveillance are offered, discuss with patients about the harms/benefits with regards to oncological outcomes and complications (Strength rating: Strong)
- Do not routinely offer thermal ablation for tumors > 3cm and cryoablation for tumors > 4 cm (Strength rating: Weak)
The following is supported by the NCCN guidelines:

Ablation is an ideal treatment option for small renal masses in (i) patients who are unfit or refuse surgery, (ii) patients with a prior ipsilateral partial nephrectomy, (iii) those with limited reserve (severe CKD, solitary kidney), (iv) those with genetic predisposition syndromes (ie. von Hippel Lindau). Outcomes of ablation are excellent, with 5 year cancer specific survival rates of ~95% for cT1a tumors. Thus, survival is often not dependent on partial nephrectomy versus radiotherapy versus ablation, but on comorbidities and competing risks of mortality.
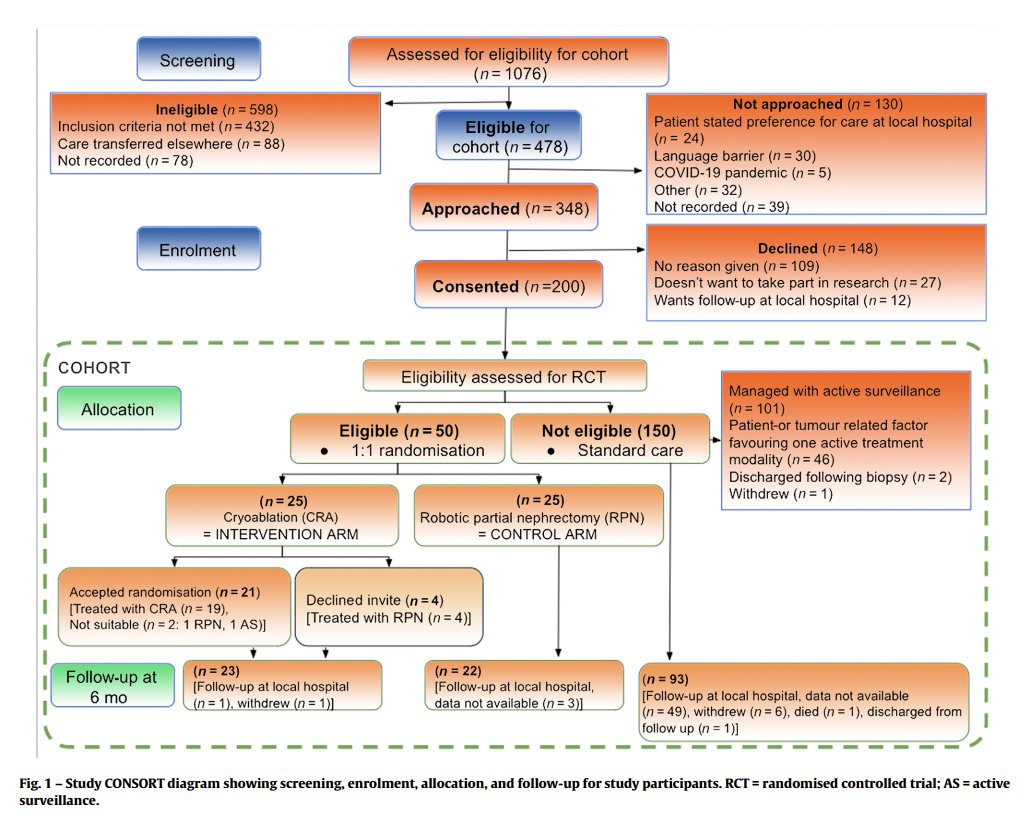
There is currently no level 1 evidence comparing modalities, with previous studies having failed to reach accrual targets (ie. SURAB, CONSERVE). The recent NEST trial demonstrated feasibility of recruiting to a cohort-embedded randomized clinical trial comparing cryoablation versus partial nephrectomy:1
For the remainder of the presentation, Dr. Bree discussed the specific ablative techniques: cryoablation, radiofrequency ablation, and microwave ablation. Starting with cryoablation, Dr. Bree discussed a study from Breen et al. [2] assessing 3- and 5-year outcomes of cryoablation in 220 patients with biopsy-proven RCC. Local recurrence free survival was 93.9% (all recurrences successfully treated with repeat ablation), metastasis free survival was 94.4%, and the major complication rate (Clavien-Dindo 3+) of 4.9%.
In a recent systematic review and meta-analysis performed by Gao et al.,3 they compared the efficacy of cryoablation versus robot-assisted partial nephrectomy in the treatment of cT1 renal tumors. This study included a total of 10 studies comprising 2,011 patients. Compared to robotic partial nephrectomy, the cryoablation group had a shorter hospital stay, less blood loss, and fewer overall complications, but a higher recurrence rate [OR 7.83; 95% CI 4.32 to 14.19; p < 0.00001]. There were no significant differences between the two groups in terms of operative time, minor complications (Clavien-Dindo Grade 1-2), major complications (Clavien-Dindo Grade 3-5), changes in renal function at 12 months post-operation, recurrence-free survival, and overall survival: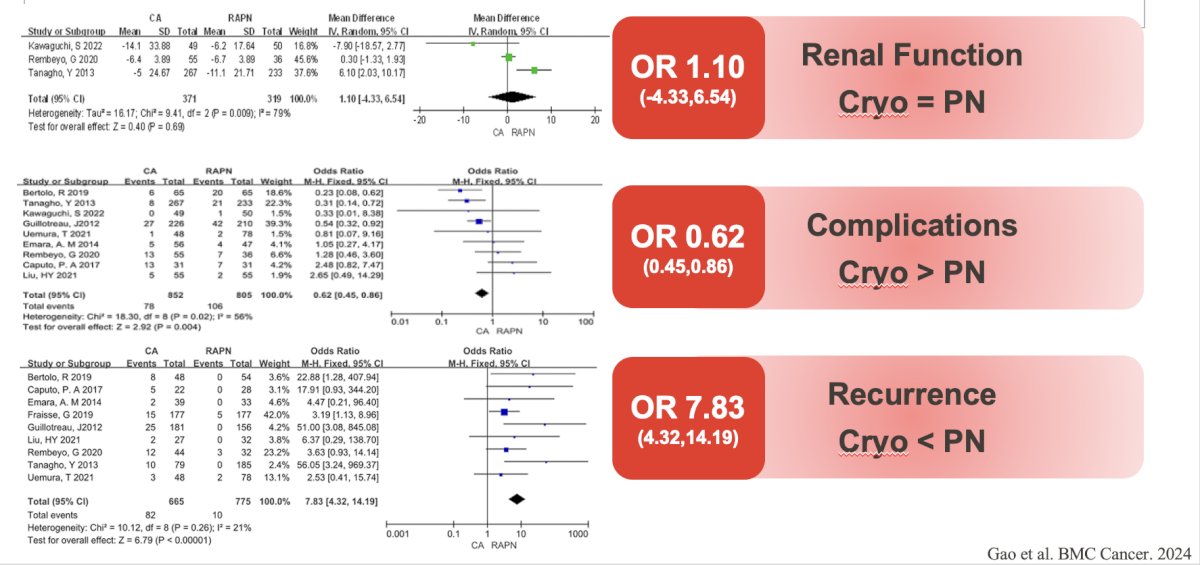
Discussing radiofrequency ablation, Dr. Bree highlighted a study from Abdelsalam et al.4 assessing the 20-year outcomes of radiofrequency ablation for solitary T1a RCC. Among 243 patients, the median tumor size was 2.5 cm, and the median follow-up was 44 months. The local recurrence free survival rate was 96.5% (ablation zone recurrences treated with ablation n = 3; partial nephrectomy n = 3; active surveillance n = 1; median time to detection: 8.5 months), metastasis free survival rate was 100%, and major complication rate (Clavien-Dindo 3+) of 4.1%. Rates of recurrence after radiofrequency ablation are higher than partial nephrectomy, however, cancer specific survival remains excellent:

Dr. Bree also noted that as a tumor increases in size by 1 cm, the likelihood of residual tumor is 2.19 times higher (95% CI 1.74 – 2.76). Moreover, cryoablation is associated with increased risk of bleeding compared to radiofrequency ablation, with the likelihood increasing with tumor size, central location, and the number of probes used. Microwave therapy is newer and less commonly used than cryoablation or radiofrequency ablation. In a small study of 26 patients, with a mean tumor size of 2.3 cm, and a median follow-up of 19.1 months, local recurrence free survival was 100%, cancer specific survival rate was 94%, and major complication rate (Clavien Dindo 3+) was high at 11.5% (included one death from complications following retroperitoneal hemorrhage, with other complications secondary to complications from bleeding after resuming anticoagulation).
At MD Anderson Cancer Center, Dr. Bree and colleagues follow the algorithm below for deciding on ablation approach:
Previous work from Andrews et al.5 assessing 1,422 patients with cT1a renal tumors demonstrates that 5-year local recurrence is rare: 97.7% for partial nephrectomy, 95.9% for radiofrequency ablation, 95.9% for cryoablation: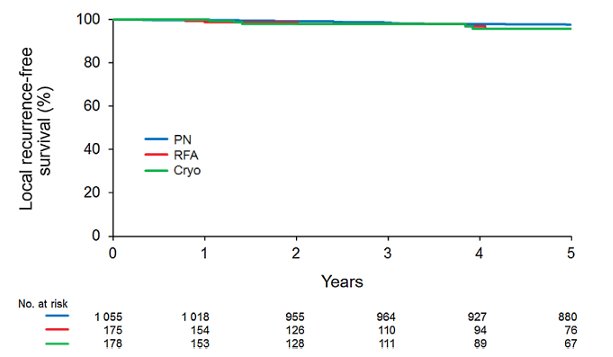
Additionally, 5-year cancer specific survival were the same in those treated with surgery versus ablation: 99.3% for partial nephrectomy, 95.6% for radiofrequency ablation, and 100% for cryoablation:

Dr. Bree concluded her presentation discussing indications and outcomes for ablation therapy in renal masses with the following take-home points:
- Ablation is a useful tool for the treatment of small renal masses: it avoids a major operation in those patients with comorbidities or a complex surgical history
- Local recurrence is rare, and when needed salvage treatment is often feasible with repeat ablation or surgery
- High grade complications are infrequent and can generally be managed without surgical intervention
- Cancer specific survival is excellent
Presented by: Kelly Bree, MD, Urologist, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX
Written by: Zachary Klaassen, MD, MSc – Urologic Oncologist, Associate Professor of Urology, Georgia Cancer Center, Wellstar MCG Health, @zklaassen_md on Twitter during the 2024 South Central American Urological Association (AUA) Annual Meeting, Colorado Springs, CO, Wed, Oct 30 – Sat, Nov 2, 2024.
References:
- Neves JB, Warren H, Santiapillai J, et al. Nephron Sparing Treatment (NEST) for Small Renal Masses: A Feasibility Cohort-embedded Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing Percutaneous Cryoablation and Robot-assisted Partial Nephrectomy. Eur Urol. 2024 Apr;85(4):333-336.
- Breen DJ, King AJ, Patel N, et al. Image-guided cryoablation for sporadic renal cell carcinoma: Three- and 5-year outcomes in 220 patients with biopsy-proven renal cell carcinoma. Radiology. 2018 Nov;289:554-561.
- Gao HY, Zhou L, Zhang JB, et al. Comparative efficacy of cryoablation versus robot-assisted partial nephrectomy in the treatment of cT1 renal tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer. 2024 Sep 16;24(1):1150.
- Abdelsalam M, Awad A, Baiomy A, et al. Outcomes of Radiofrequency Ablation for Solitary T1a Renal Cell Carcinoma: A 20-Year Tertiary Cancer Center Experience. Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jan 31;15(3):909.
- Andrews JR, Atwell T, Schmit G, et al. Oncologic outcomes following partial nephrectomy and percutaneous ablation for cT1 renal masses. Eur Urol. 2019 Aug;76(2):244-251.










